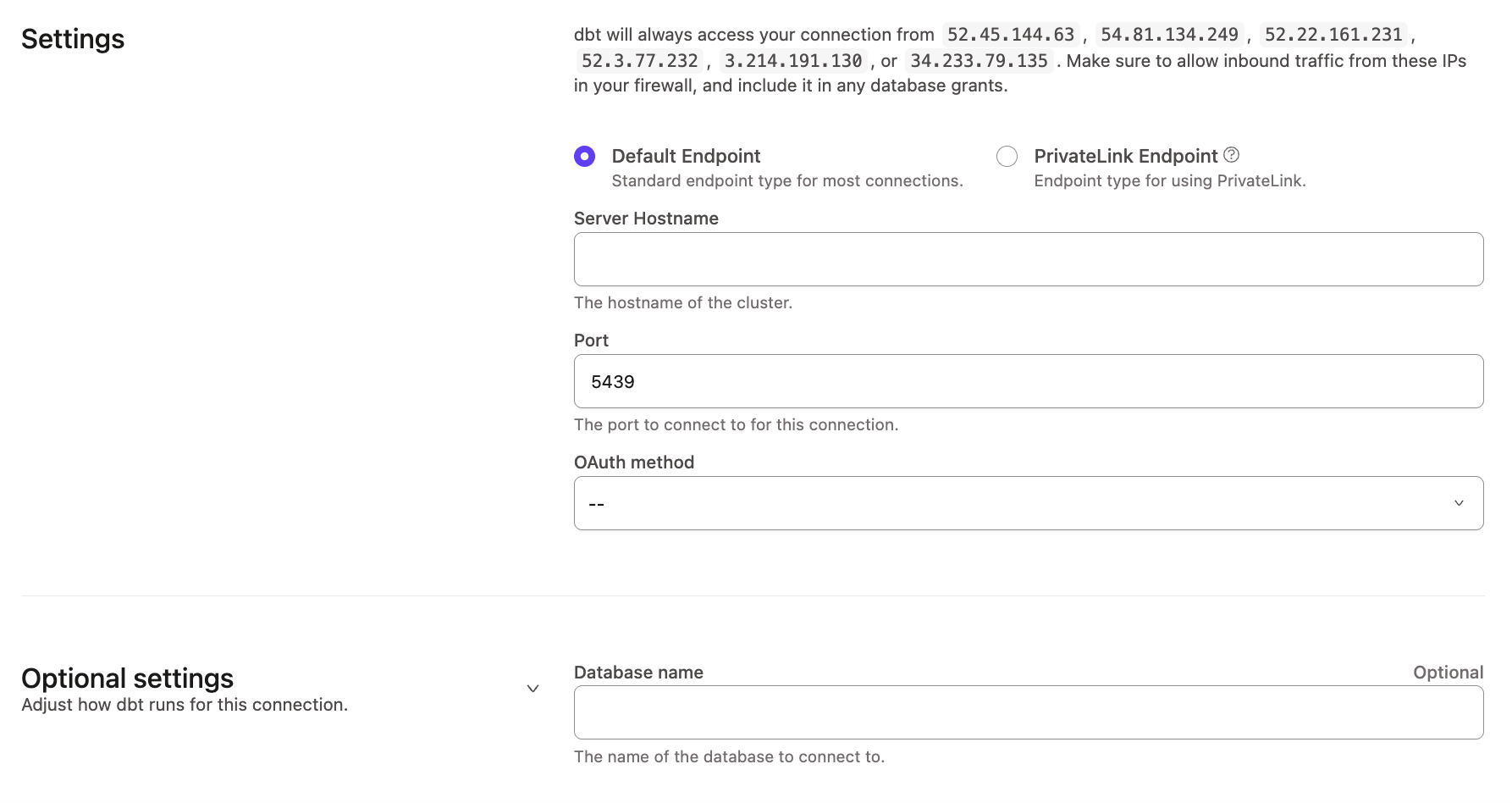
Connect Redshift, PostgreSQL, Lakebase and AlloyDB
dbt Platform supports connecting to PostgresSQL, Postgres-compatible databases (AlloyDB, Lakebase), and Redshift.
The following fields are required when creating a connection:
| Field | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Host Name | The hostname of the database to connect to. This can either be a hostname or an IP address. Refer to set up pages to find the hostname for your adapter. | Postgres: xxx.us-east-1.amazonaws.com |
| Port | Usually 5432 (Postgres) or 5439 (Redshift) | 5439 |
| Database | The logical database to connect to and run queries against. | analytics |
Note: When you set up a Redshift or Postgres connection in dbt, SSL-related parameters aren't available as inputs.
Authentication Parameters
For authentication, dbt users can use Database username and password for Postgres and Postgres compatible databases. For more information on what is supported, check out the database specific setup page for limitations and helpful tips.
In addition, for Redshift, users can use IAM User authentication via extended attributes or Identity Center via external Oauth. IAM role authentication is not supported.
- Database
- IAM User
The following table contains the parameters for the database (password-based) connection method.
| Field | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
user | Account username to log into your cluster | myuser |
password | Password for authentication | _password1! |
On Cloud, the IAM user authentication is currently only supported via extended attributes. Once the project is created, development and deployment environments can be updated to use extended attributes to pass the fields described below, as some are not supported via textbox.
You will need to create an IAM User, generate an access key, and either:
- on a cluster, a database user is expected in the
userfield. The IAM user is only leveraged for authentication, the database user for authorization - on Serverless, grant permission to the IAM user in Redshift. The
userfield is ignored (but still required) - For both, the
passwordfield will be ignored.
| Profile field | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
method | IAM | use IAM to authenticate via IAM User authentication |
cluster_id | CLUSTER_ID | Required for IAM authentication only for provisoned cluster, not for Serverless |
user | username | User querying the database, ignored for Serverless (but still required) |
region | us-east-1 | Region of your Redshift instance |
access_key_id | ACCESS_KEY_ID | IAM user access key id |
secret_access_key | SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | IAM user secret access key |
Example Extended Attributes for IAM User on Redshift Serverless
To avoid pasting secrets in extended attributes, leverage environment variables:
host: my-production-instance.myregion.redshift-serverless.amazonaws.com
method: iam
region: us-east-2
access_key_id: '{{ env_var(''DBT_ENV_ACCESS_KEY_ID'') }}'
secret_access_key: '{{ env_var(''DBT_ENV_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY'') }}'
Both DBT_ENV_ACCESS_KEY_ID and DBT_ENV_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY will need to be assigned for every environment leveraging extended attributes as such.
Connecting via an SSH Tunnel
To connect to a Postgres, Redshift, or AlloyDB instance via an SSH tunnel, select the Use SSH Tunnel option when creating your connection. When configuring the tunnel, you must supply the hostname, username, and port for the bastion server.
Once the connection is saved, a public key will be generated and displayed for the Connection. You can copy this public key to the bastion server to authorize dbt to connect to your database via the bastion server.
About the Bastion server in AWS
What is a Bastion server?
A bastion server in Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a host that allows dbt to open an SSH connection.
dbt only sends queries and doesn't transmit large data volumes. This means the bastion server can run on an AWS instance of any size, like a t2.small instance or t2.micro.
Make sure the location of the instance is the same Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) as the Redshift instance, and configure the security group for the bastion server to ensure that it's able to connect to the warehouse port.
Configuring the Bastion Server in AWS
To configure the SSH tunnel in dbt, you'll need to provide the hostname/IP of your bastion server, username, and port, of your choosing, that dbt will connect to. Review the following steps:
- Verify the bastion server has its network security rules set up to accept connections from the dbt IP addresses on whatever port you configured.
- Set up the user account by using the bastion servers instance's CLI, The following example uses the username
dbtcloud:
sudo groupadd dbtcloud
sudo useradd -m -g dbtcloud dbtcloud
sudo su - dbtcloud
mkdir ~/.ssh
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
- Copy and paste the dbt generated public key, into the authorized_keys file.
The Bastion server should now be ready for dbt to use as a tunnel into the Redshift environment.
Configuration
To optimize performance with data platform-specific configurations in dbt, refer to Redshift-specific configuration.
To grant users or roles database permissions (access rights and privileges), refer to the Redshift permissions page or Postgres permissions page.
FAQs
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.