About the Studio IDE
The dbt integrated development environment (Studio IDE) is a single web-based interface for building, testing, running, and version-controlling dbt projects. It compiles dbt code into SQL and executes it directly on your database.
The Studio IDE offers several keyboard shortcuts and editing features for faster and efficient development and governance:
- Syntax highlighting for SQL — Makes it easy to distinguish different parts of your code, reducing syntax errors and enhancing readability.
- AI copilot — Use Copilot, an AI-powered assistant that can generate code using natural language, and generate resources (like documentation, tests, and semantic models) for you — with the click of a button. Check out Develop with Copilot for more details.
- Auto-completion — Suggests table names, arguments, and column names as you type, saving time and reducing typos.
- Code formatting and linting — Helps standardize and fix your SQL code effortlessly.
- Navigation tools — Easily move around your code, jump to specific lines, find and replace text, and navigate between project files.
- Version control — Manage code versions with a few clicks.
- Project documentation — Generate and view your project documentation for your dbt project in real-time.
- Build, test, and run button — Build, test, and run your project with a button click or by using the Studio IDE command bar.
These features create a powerful editing environment for efficient SQL coding, suitable for both experienced and beginner developers.
To improve your experience using dbt, we suggest that you turn off ad blockers. This is because some project file names, such as google_adwords.sql, might resemble ad traffic and trigger ad blockers.
Prerequisites
- A dbt account and Developer seat license
- A git repository set up and git provider must have
writeaccess enabled. See Connecting your GitHub Account or Importing a project by git URL for detailed setup instructions - A dbt project connected to a data platform
- A development environment and development credentials set up
- The environment must be on dbt version 1.0 or higher
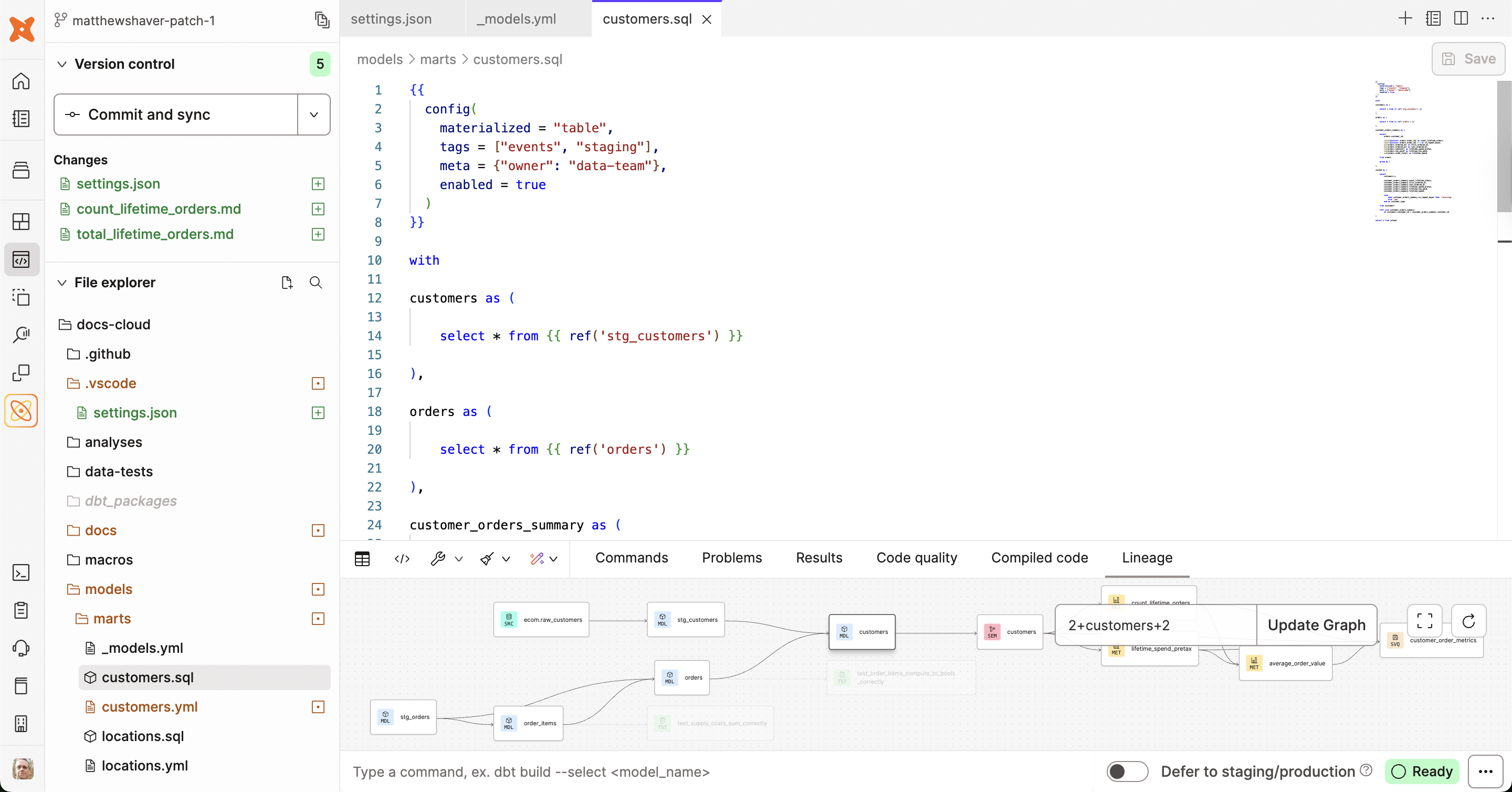
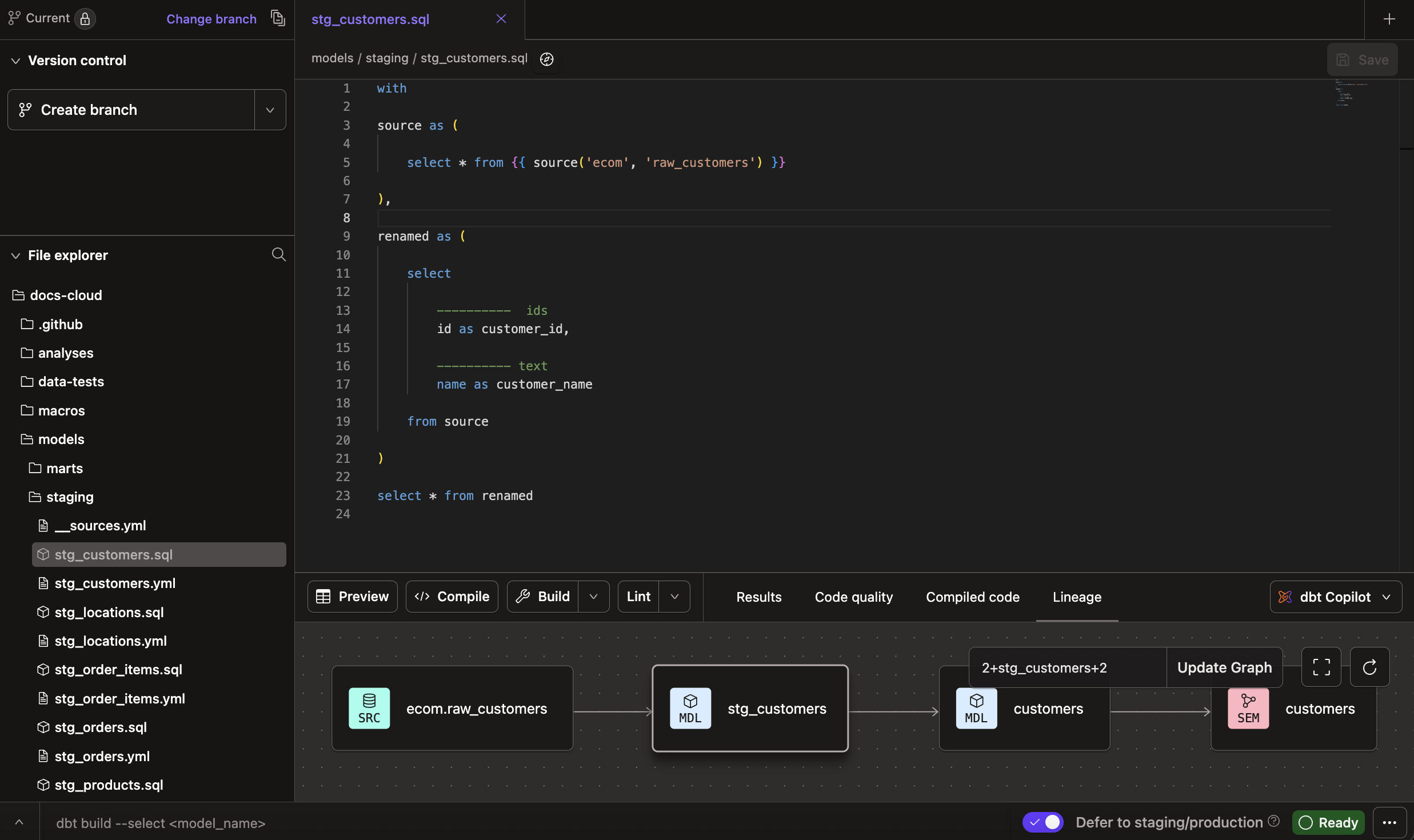
Studio IDE features
The Studio IDE comes with features that make it easier for you to develop, build, compile, run, and test data models.
To understand how to navigate the Studio IDE and its user interface elements, refer to the Studio IDE user interface page.
| Loading table... |
Code generation
The Studio IDE comes with CodeGenCodeLens, a powerful feature that simplifies creating models from your sources with a click of a button. To use this feature, click on the Generate model action next to each table in the source YAML file(s). It automatically creates a basic starting staging model for you to expand on. This feature helps streamline your workflow by automating the first steps of model generation.
dbt YAML validation
Use dbt-jsonschema to validate dbt YAML files, helping you leverage the autocomplete and assistance capabilities of the Studio IDE. This also provides immediate feedback on YAML file structure and syntax, helping you make sure your project configurations meet the required standards.
Get started with the Studio IDE
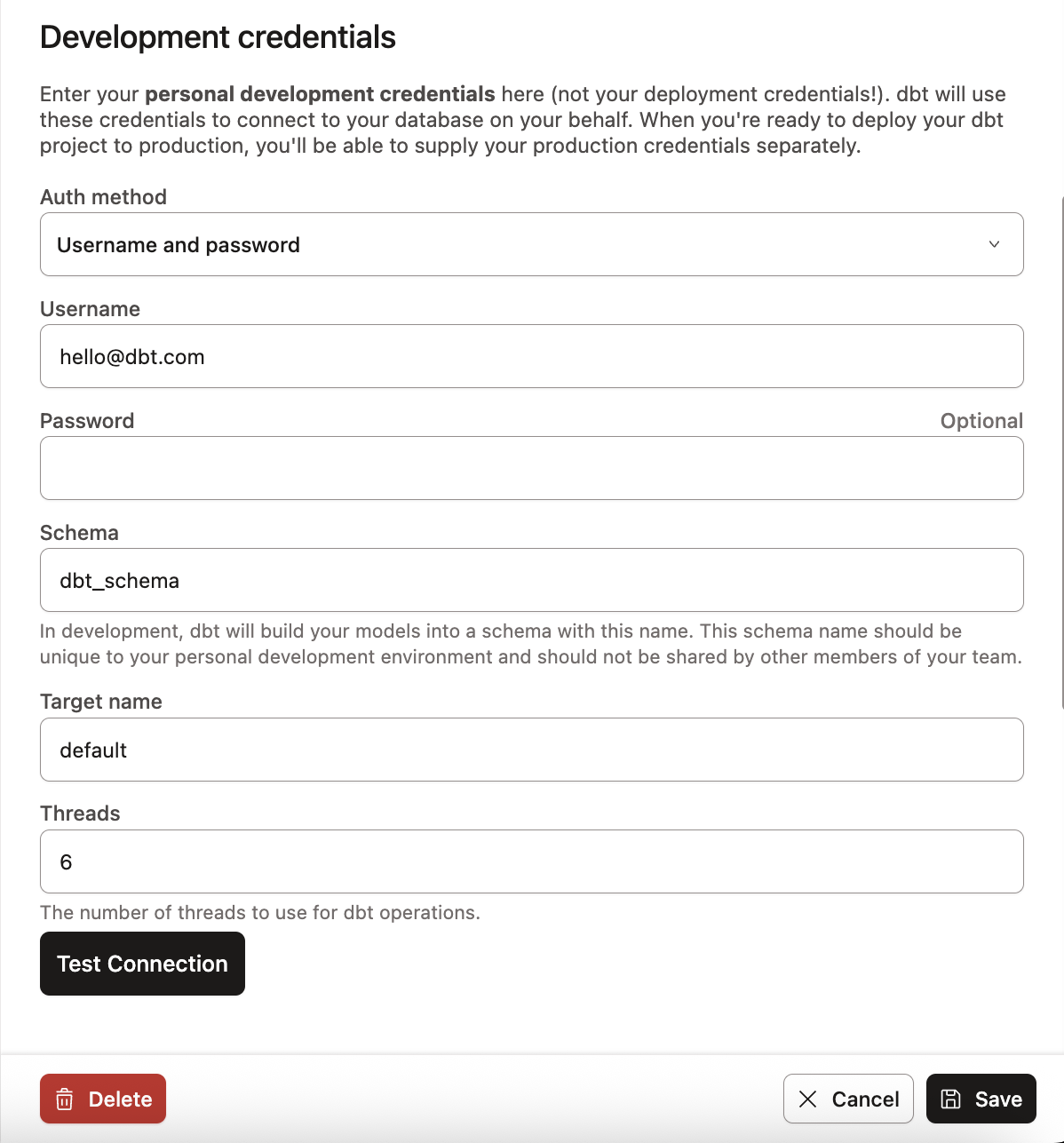
In order to start experiencing the great features of the Studio IDE, you need to first set up a dbt development environment. In the following steps, we outline how to set up developer credentials and access the Studio IDE. If you're creating a new project, you will automatically configure this during the project setup.
The Studio IDE uses developer credentials to connect to your data platform. These developer credentials should be specific to your user and they should not be super user credentials or the same credentials that you use for your production deployment of dbt.
Set up your developer credentials:
- Navigate to your Credentials under Your Profile settings, which you can access at
https://YOUR_ACCESS_URL/settings/profile#credentials, replacingYOUR_ACCESS_URLwith the appropriate Access URL for your region and plan. - Select the relevant project in the list.
- Click Edit on the bottom right of the page.
- Enter the details under Development Credentials.
- Click Save.
- Navigate to the Studio IDE by clicking Studio in the left menu.
- Initialize your project and familiarize yourself with the Studio IDE and its delightful features.
Nice job, you're ready to start developing and building models 🎉!
Considerations
-
To improve your experience using dbt, we suggest that you turn off ad blockers. This is because some project file names, such as
google_adwords.sql, might resemble ad traffic and trigger ad blockers. -
To preserve performance, there's a file size limitation for repositories over 6 GB. If you have a repo over 6 GB, please contact dbt Support before running dbt.
-
The Studio IDE's idle session timeout is one hour.
Build and document your projects
-
Build, compile, and run projects — You can build, compile, run, and test dbt projects using the command bar or Build button. Use the Build button to quickly build, run, or test the model you're working on. The Studio IDE will update in real time when you run models, tests, seeds, and operations.
- If a model or test fails, dbt makes it easy for you to view and download the run logs for your dbt invocations to fix the issue.
- Use dbt's rich model selection syntax to run dbt commands directly within dbt.
- Leverage environments variables to dynamically use the Git branch name. For example, using the branch name as a prefix for a development schema.
- Run MetricFlow commands to create and manage metrics in your project with the Semantic Layer.
-
Generate your YAML configurations with Copilot — dbt Copilot is a powerful artificial intelligence (AI) feature that helps automate development in dbt. It can generate code using natural language, and generate resources (like documentation, tests, metrics,and semantic models) for you directly in the Studio IDE, so you can accomplish more in less time. StarterEnterpriseEnterprise +
-
Build and view your project's docs — The Studio IDE makes it possible to build and view documentation for your dbt project while your code is still in development. With this workflow, you can inspect and verify what your project's generated documentation will look like before your changes are released to production.
Related docs
FAQs
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.