Develop with dbt Copilot StarterEnterpriseEnterprise +
This page describes how to use Copilot in the Studio IDE to improve your development workflow.
Use Copilot in the Studio IDE to generate documentation, tests, semantic models, metrics, and SQL code from scratch — making it easier for you to build your dbt project, accelerate your development, and focus on high-level tasks. For information about using Copilot in the Canvas, see Build with Copilot.
Generate resources
Generate documentation, tests, metrics, and semantic models resources with the click-of-a-button in the Studio IDE using dbt Copilot, saving you time. To access and use this AI feature:
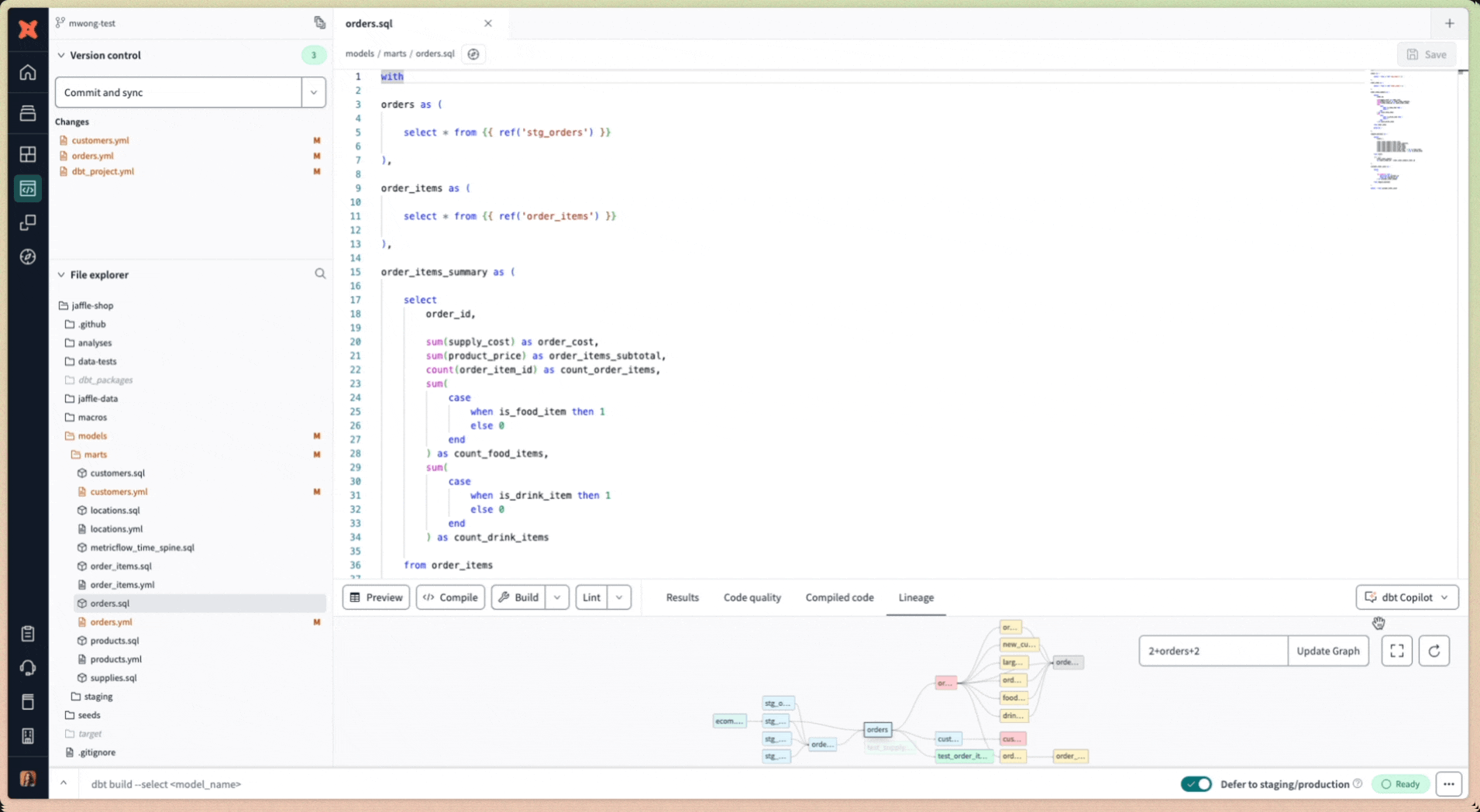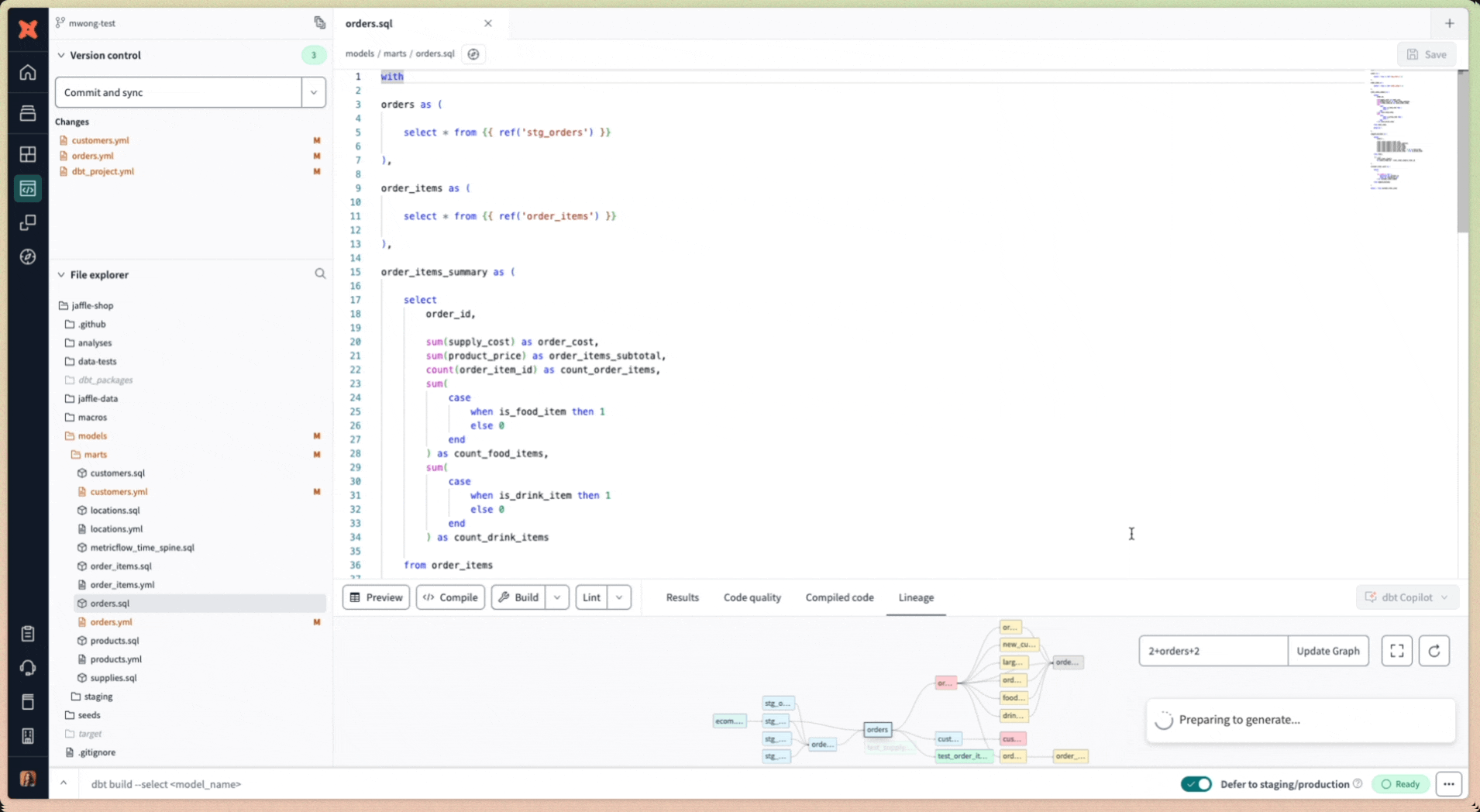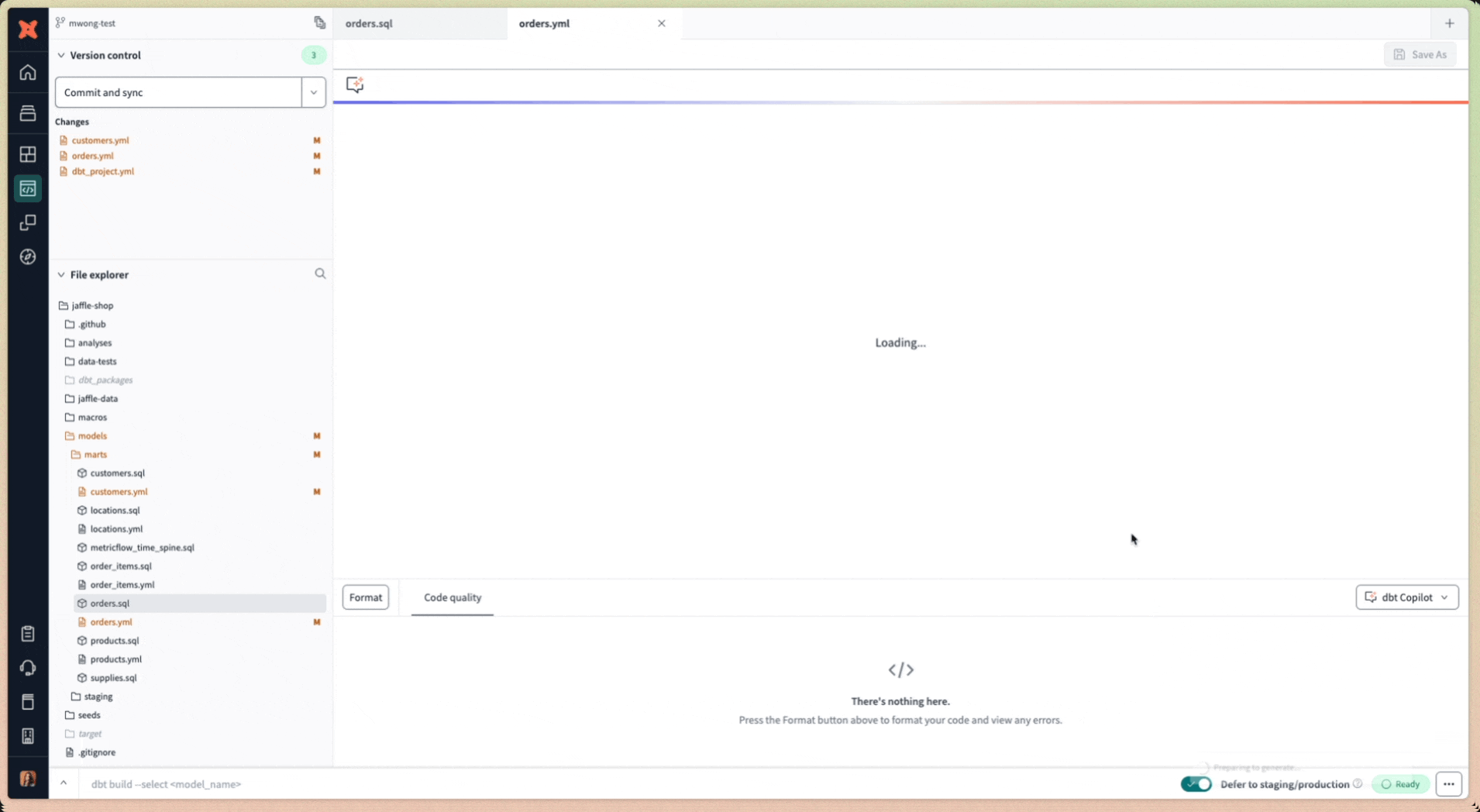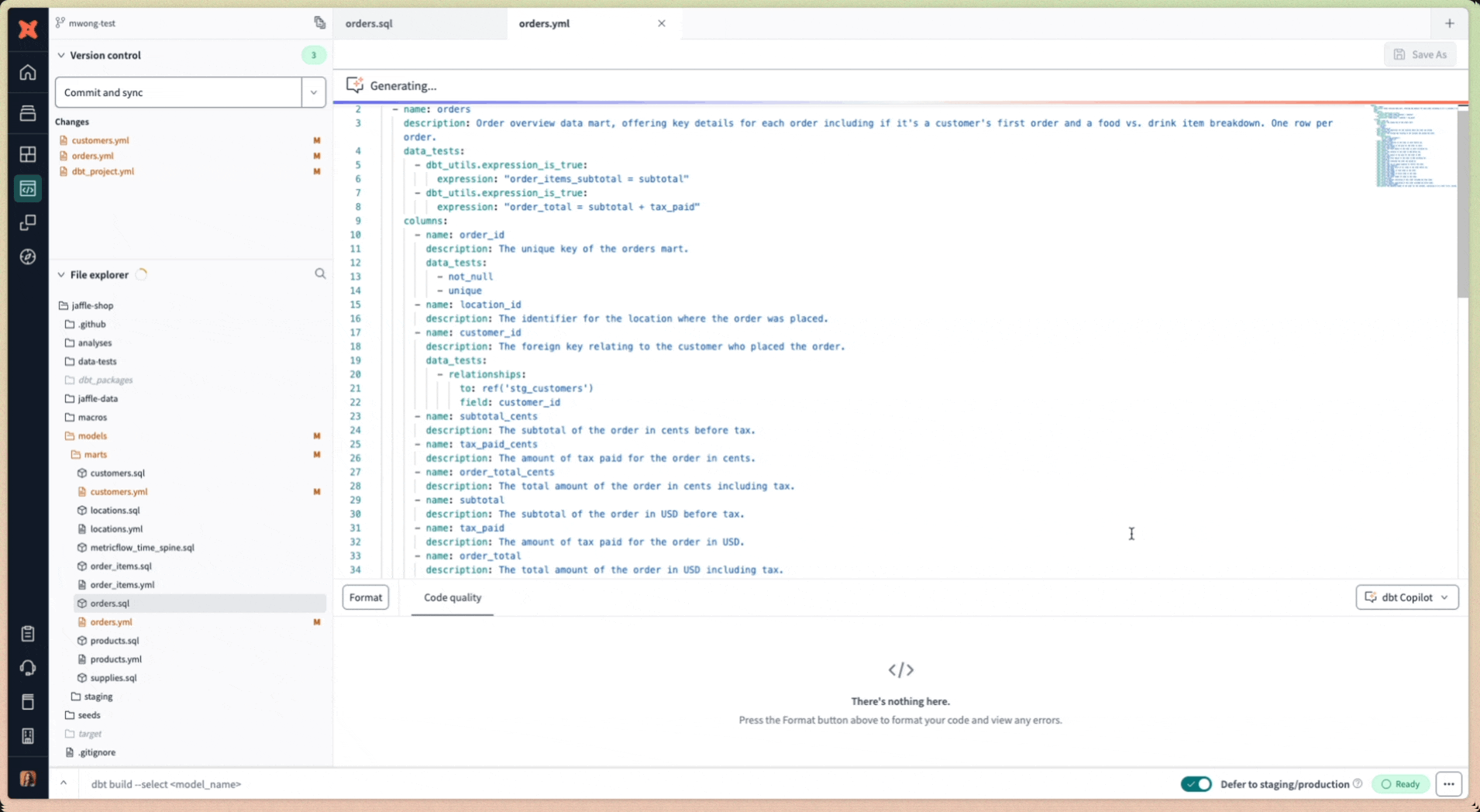
- Navigate to the Studio IDE and select a SQL model file under the File Explorer.
- In the Console section (under the File Editor), click dbt Copilot to view the available AI options.
- Select the available options to generate the YAML config: Generate Documentation, Generate Tests, Generate Semantic Model, or Generate Metrics. To generate multiple YAML configs for the same model, click each option separately. dbt Copilot intelligently saves the YAML config in the same file.
- To generate metrics, you need to first have semantic models defined.
- Once defined, click dbt Copilot and select Generate Metrics.
- Write a prompt describing the metrics you want to generate and press enter.
- Accept or Reject the generated code.
- Verify the AI-generated code. You can update or fix the code as needed.
- Click Save As. You should see the file changes under the Version control section.
Generate and edit code
Copilot also allows you to generate SQL code directly within the SQL file in the Studio IDE, using natural language prompts. This means you can rewrite or add specific portions of the SQL file without needing to edit the entire file.
This intelligent AI tool streamlines SQL development by reducing errors, scaling effortlessly with complexity, and saving valuable time. Copilot's prompt window, accessible by keyboard shortcut, handles repetitive or complex SQL generation effortlessly so you can focus on high-level tasks.
Use Copilot's prompt window for use cases like:
- Writing advanced transformations
- Performing bulk edits efficiently
- Crafting complex patterns like regex
Use the prompt window
Access Copilot's AI prompt window using the keyboard shortcut Cmd+B (Mac) or Ctrl+B (Windows) to:
1. Generate SQL from scratch
- Use the keyboard shortcuts Cmd+B (Mac) or Ctrl+B (Windows) to generate SQL from scratch.
- Enter your instructions to generate SQL code tailored to your needs using natural language.
- Ask Copilot to fix the code or add a specific portion of the SQL file.
2. Edit existing SQL code
- Highlight a section of SQL code and press Cmd+B (Mac) or Ctrl+B (Windows) to open the prompt window for editing.
- Use this to refine or modify specific code snippets based on your needs.
- Ask Copilot to fix the code or add a specific portion of the SQL file.
3. Review changes with the diff view to quickly assess the impact of the changes before making changes
- When a suggestion is generated, Copilot displays a visual "diff" view to help you compare the proposed changes with your existing code:
- Green: Means new code that will be added if you accept the suggestion.
- Red: Highlights existing code that will be removed or replaced by the suggested changes.
4. Accept or reject suggestions
- Accept: If the generated SQL meets your requirements, click the Accept button to apply the changes directly to your
.sqlfile directly in the IDE. - Reject: If the suggestion don’t align with your request/prompt, click Reject to discard the generated SQL without making changes and start again.
5. Regenerate code
- To regenerate, press the Escape button on your keyboard (or click the Reject button in the popup). This will remove the generated code and puts your cursor back into the prompt text area.
- Update your prompt and press Enter to try another generation. Press Escape again to close the popover entirely.
Once you've accepted a suggestion, you can continue to use the prompt window to generate additional SQL code and commit your changes to the branch.
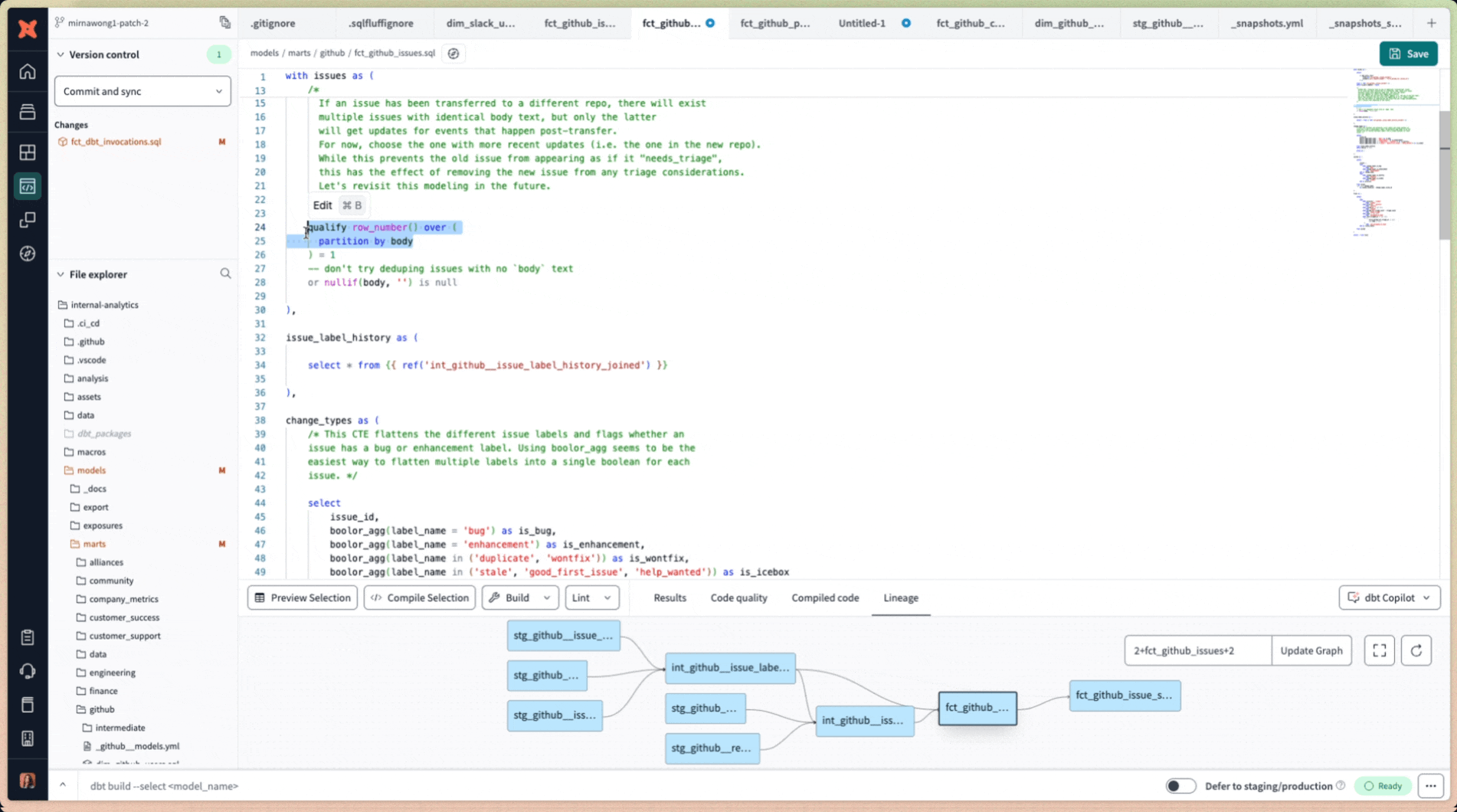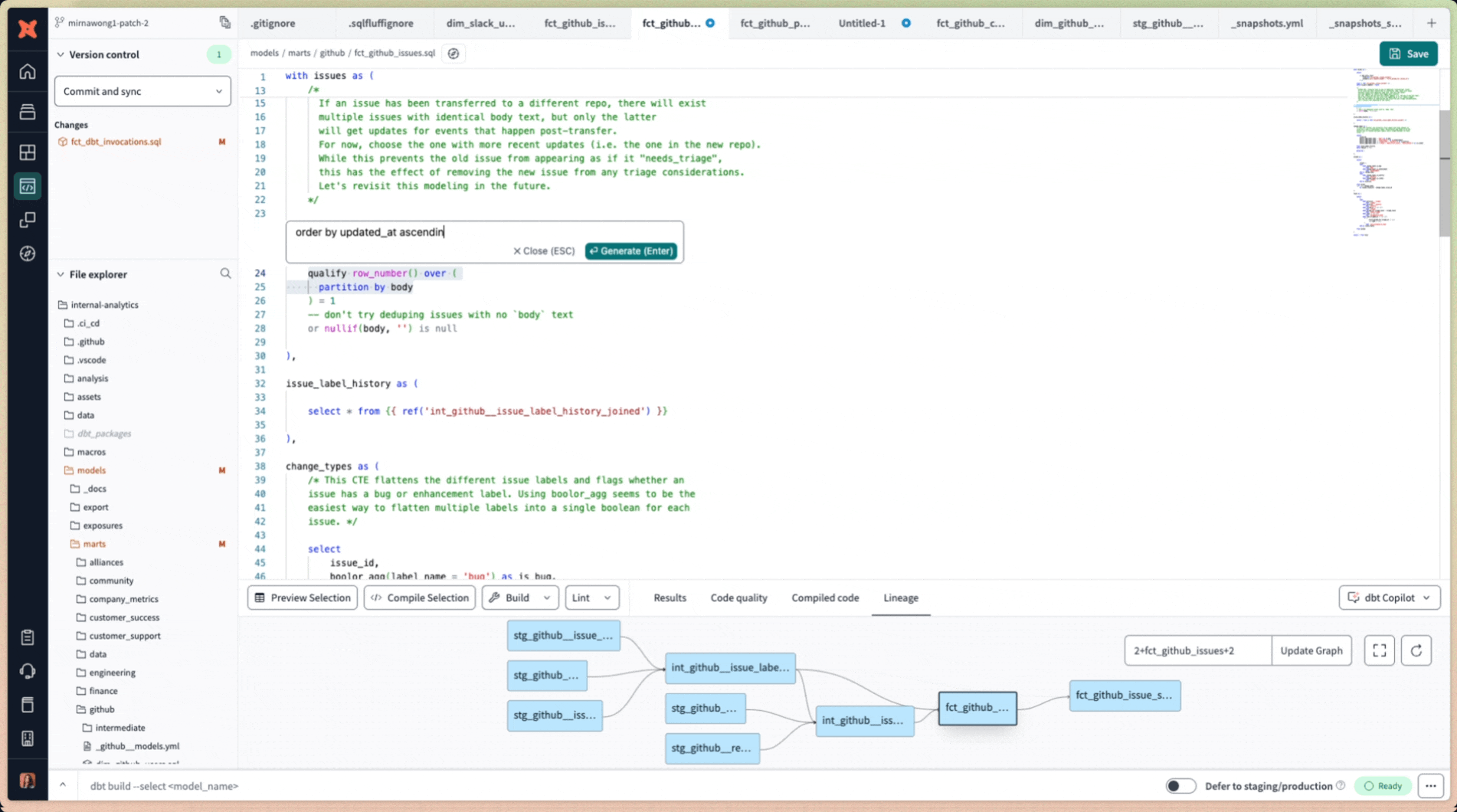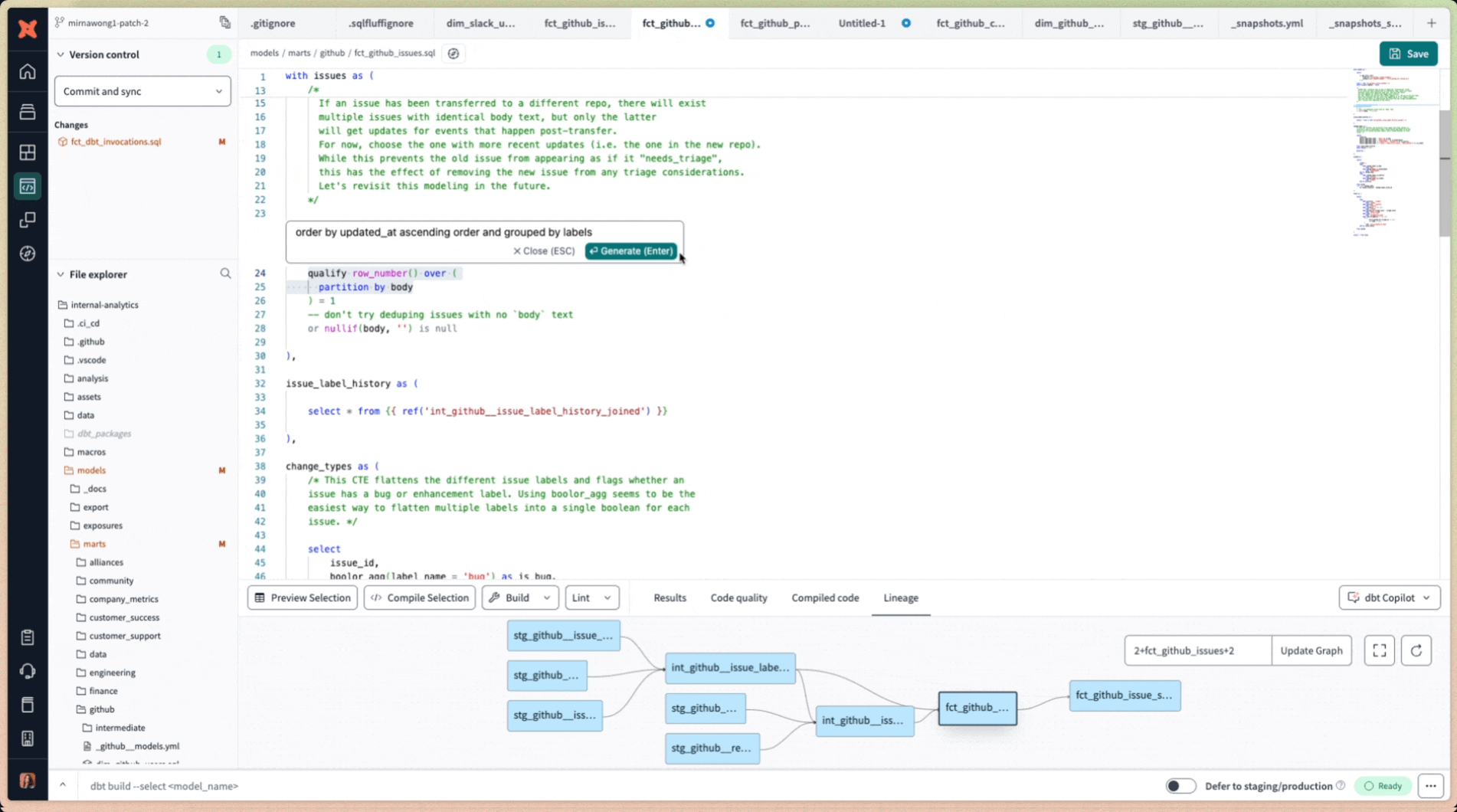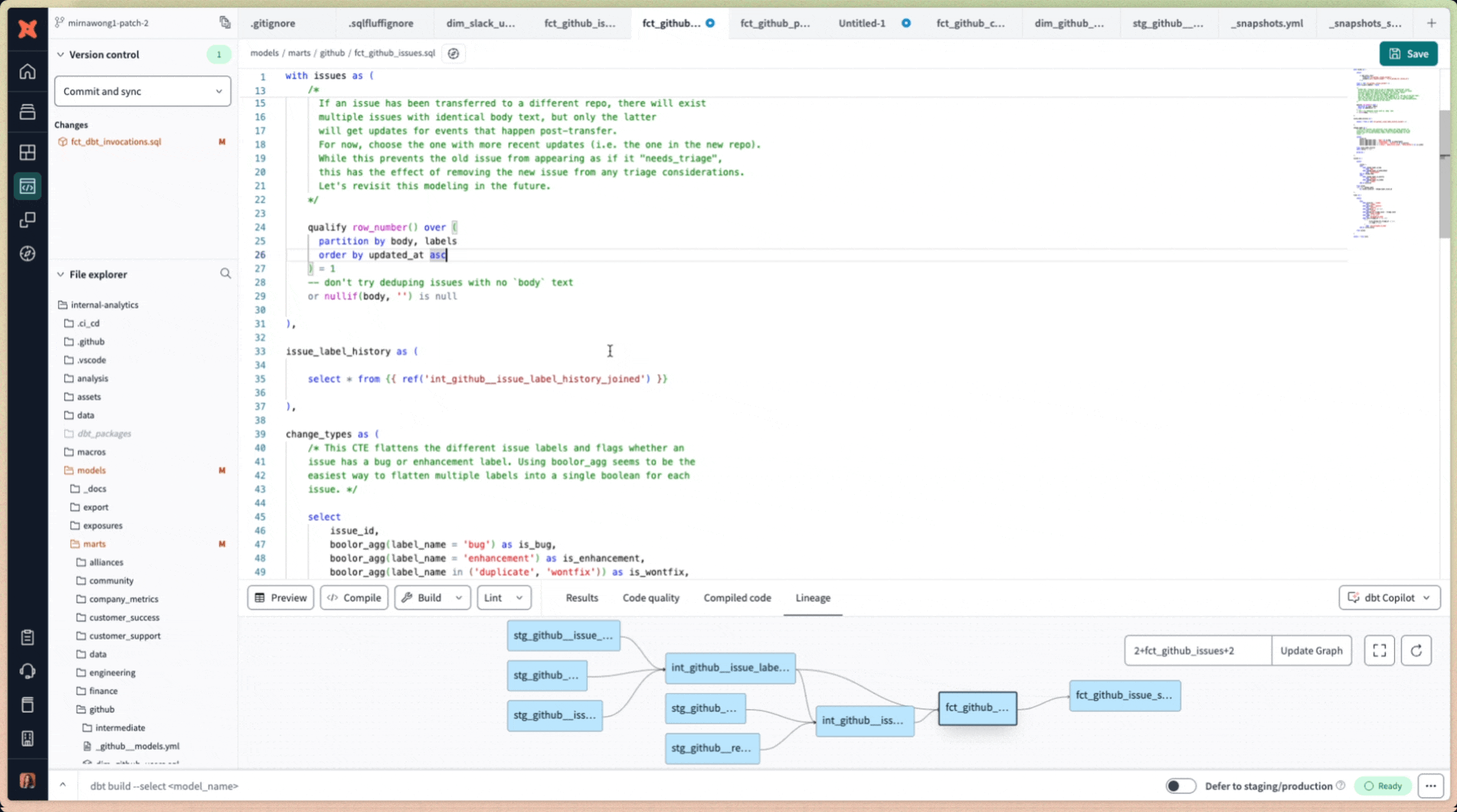 Edit existing SQL code using dbt Copilot's prompt window accessible by keyboard shortcut Cmd+B (Mac) or Ctrl+B (Windows)
Edit existing SQL code using dbt Copilot's prompt window accessible by keyboard shortcut Cmd+B (Mac) or Ctrl+B (Windows)Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.