Quickstart for dbt and BigQuery
Introduction
In this quickstart guide, you'll learn how to use dbt with BigQuery. It will show you how to:
- Create a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) project.
- Access sample data in a public dataset.
- Connect dbt to BigQuery.
- Take a sample query and turn it into a model in your dbt project. A model in dbt is a select statement.
- Add tests to your models.
- Document your models.
- Schedule a job to run.
You can check out dbt Fundamentals for free if you're interested in course learning with videos.
Prerequisites
- You have a dbt account.
- You have a Google account.
- You can use a personal or work account to set up BigQuery through Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Related content
- Learn more with dbt Learn courses
- CI jobs
- Deploy jobs
- Job notifications
- Source freshness
Create a new GCP project
- Go to the BigQuery Console after you log in to your Google account. If you have multiple Google accounts, make sure you’re using the correct one.
- Create a new project from the Manage resources page. For more information, refer to Creating a project in the Google Cloud docs. GCP automatically populates the Project name field for you. You can change it to be more descriptive for your use. For example,
dbt Learn - BigQuery Setup.
Create BigQuery datasets
-
From the BigQuery Console, click Editor. Make sure to select your newly created project, which is available at the top of the page.
-
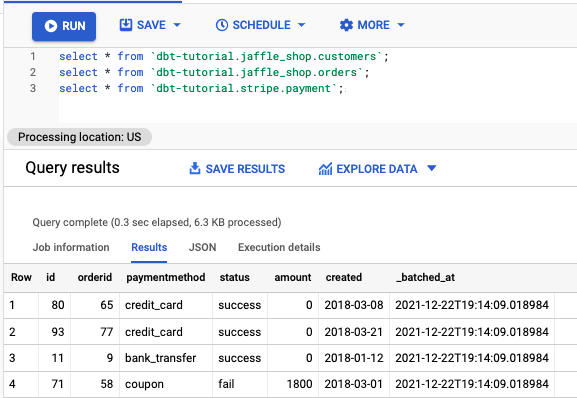
Verify that you can run SQL queries. Copy and paste these queries into the Query Editor:
select * from `dbt-tutorial.jaffle_shop.customers`;
select * from `dbt-tutorial.jaffle_shop.orders`;
select * from `dbt-tutorial.stripe.payment`;Click Run, then check for results from the queries. For example:
-
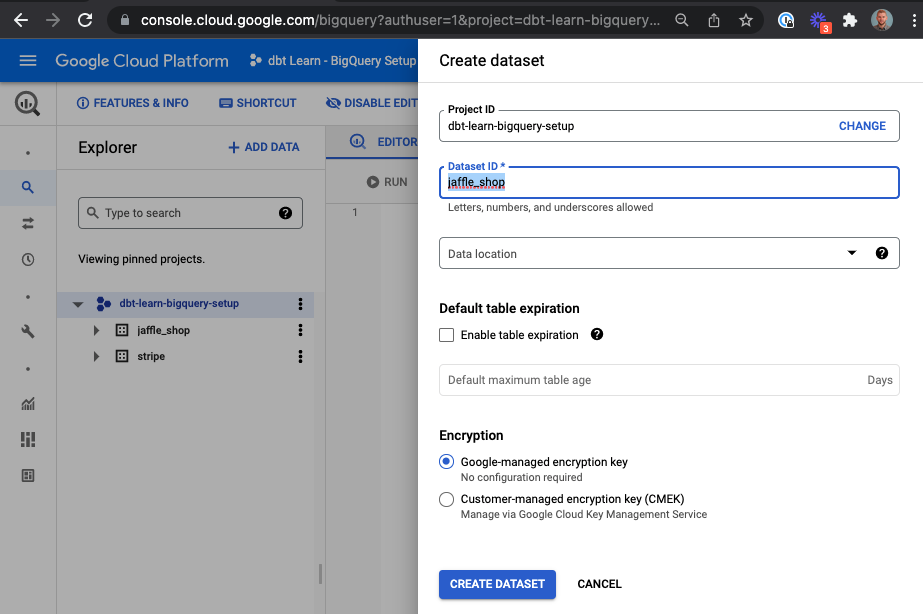
Create new datasets from the BigQuery Console. For more information, refer to Create datasets in the Google Cloud docs. Datasets in BigQuery are equivalent to schemas in a traditional database. On the Create dataset page:
- Dataset ID — Enter a name that fits the purpose. This name is used like schema in fully qualified references to your database objects such as
database.schema.table. As an example for this guide, create one forjaffle_shopand another one forstripeafterward. - Data location — Leave it blank (the default). It determines the GCP location of where your data is stored. The current default location is the US multi-region. All tables within this dataset will share this location.
- Enable table expiration — Leave it unselected (the default). The default for the billing table expiration is 60 days. Because billing isn’t enabled for this project, GCP defaults to deprecating tables.
- Google-managed encryption key — This option is available under Advanced options. Allow Google to manage encryption (the default).
- Dataset ID — Enter a name that fits the purpose. This name is used like schema in fully qualified references to your database objects such as
-
After you create the
jaffle_shopdataset, create one forstripewith all the same values except for Dataset ID.
Generate BigQuery credentials
In order to let dbt connect to your warehouse, you'll need to generate a keyfile. This is analogous to using a database username and password with most other data warehouses.
- Start the GCP credentials wizard. Make sure your new project is selected in the header. If you do not see your account or project, click your profile picture to the right and verify you are using the correct email account. For Credential Type:
- From the Select an API dropdown, choose BigQuery API
- Select Application data for the type of data you will be accessing
- Click Next to create a new service account.
- Create a service account for your new project from the Service accounts page. For more information, refer to Create a service account in the Google Cloud docs. As an example for this guide, you can:
- Type
dbt-useras the Service account name - From the Select a role dropdown, choose BigQuery Job User and BigQuery Data Editor roles and click Continue
- Leave the Grant users access to this service account fields blank
- Click Done
- Type
- Create a service account key for your new project from the Service accounts page. For more information, refer to Create a service account key in the Google Cloud docs. When downloading the JSON file, make sure to use a filename you can easily remember. For example,
dbt-user-creds.json. For security reasons, dbt Labs recommends that you protect this JSON file like you would your identity credentials; for example, don't check the JSON file into your version control software.
Connect dbt to BigQuery
- Create a new project in dbt. Navigate to Account settings (by clicking on your account name in the left side menu), and click + New project.
- Enter a project name and click Continue.
- For the warehouse, click BigQuery then Next to set up your connection.
- Click Upload a Service Account JSON File in settings.
- Select the JSON file you downloaded in Generate BigQuery credentials and dbt will fill in all the necessary fields.
- Optional — dbt Enterprise plans can configure developer OAuth with BigQuery, providing an additional layer of security. For more information, refer to Set up BigQuery OAuth.
- Click Test Connection. This verifies that dbt can access your BigQuery account.
- Click Next if the test succeeded. If it failed, you might need to go back and regenerate your BigQuery credentials.
Set up a dbt managed repository
When you develop in dbt, you can leverage Git to version control your code.
To connect to a repository, you can either set up a dbt-hosted managed repository or directly connect to a supported git provider. Managed repositories are a great way to trial dbt without needing to create a new repository. In the long run, it's better to connect to a supported git provider to use features like automation and continuous integration.
To set up a managed repository:
- Under "Setup a repository", select Managed.
- Type a name for your repo such as
bbaggins-dbt-quickstart - Click Create. It will take a few seconds for your repository to be created and imported.
- Once you see the "Successfully imported repository," click Continue.
Initialize your dbt project and start developing
Now that you have a repository configured, you can initialize your project and start development in dbt:
- Click Start developing in the Studio IDE. It might take a few minutes for your project to spin up for the first time as it establishes your git connection, clones your repo, and tests the connection to the warehouse.
- Above the file tree to the left, click Initialize dbt project. This builds out your folder structure with example models.
- Make your initial commit by clicking Commit and sync. Use the commit message
initial commitand click Commit. This creates the first commit to your managed repo and allows you to open a branch where you can add new dbt code. - You can now directly query data from your warehouse and execute
dbt run. You can try this out now:- Click + Create new file, add this query to the new file, and click Save as to save the new file:
select * from `dbt-tutorial.jaffle_shop.customers` - In the command line bar at the bottom, enter
dbt runand click Enter. You should see adbt run succeededmessage.
- Click + Create new file, add this query to the new file, and click Save as to save the new file:
Build your first model
You have two options for working with files in the Studio IDE:
- Create a new branch (recommended) — Create a new branch to edit and commit your changes. Navigate to Version Control on the left sidebar and click Create branch.
- Edit in the protected primary branch — If you prefer to edit, format, or lint files and execute dbt commands directly in your primary git branch. The Studio IDE prevents commits to the protected branch, so you will be prompted to commit your changes to a new branch.
Name the new branch add-customers-model.
- Click the ... next to the
modelsdirectory, then select Create file. - Name the file
customers.sql, then click Create. - Copy the following query into the file and click Save.
with customers as (
select
id as customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
from `dbt-tutorial`.jaffle_shop.customers
),
orders as (
select
id as order_id,
user_id as customer_id,
order_date,
status
from `dbt-tutorial`.jaffle_shop.orders
),
customer_orders as (
select
customer_id,
min(order_date) as first_order_date,
max(order_date) as most_recent_order_date,
count(order_id) as number_of_orders
from orders
group by 1
),
final as (
select
customers.customer_id,
customers.first_name,
customers.last_name,
customer_orders.first_order_date,
customer_orders.most_recent_order_date,
coalesce(customer_orders.number_of_orders, 0) as number_of_orders
from customers
left join customer_orders using (customer_id)
)
select * from final
- Enter
dbt runin the command prompt at the bottom of the screen. You should get a successful run and see the three models.
Later, you can connect your business intelligence (BI) tools to these views and tables so they only read cleaned up data rather than raw data in your BI tool.
FAQs
Change the way your model is materialized
One of the most powerful features of dbt is that you can change the way a model is materialized in your warehouse, simply by changing a configuration value. You can change things between tables and views by changing a keyword rather than writing the data definition language (DDL) to do this behind the scenes.
By default, everything gets created as a view. You can override that at the directory level so everything in that directory will materialize to a different materialization.
-
Edit your
dbt_project.ymlfile.-
Update your project
nameto:dbt_project.ymlname: 'jaffle_shop' -
Configure
jaffle_shopso everything in it will be materialized as a table; and configureexampleso everything in it will be materialized as a view. Update yourmodelsconfig in the project YAML file to:dbt_project.ymlmodels:
jaffle_shop:
+materialized: table
example:
+materialized: view -
Click Save.
-
-
Enter the
dbt runcommand. Yourcustomersmodel should now be built as a table!infoTo do this, dbt had to first run a
drop viewstatement (or API call on BigQuery), then acreate table asstatement. -
Edit
models/customers.sqlto override thedbt_project.ymlfor thecustomersmodel only by adding the following snippet to the top, and click Save:models/customers.sql{{
config(
materialized='view'
)
}}
with customers as (
select
id as customer_id
...
) -
Enter the
dbt runcommand. Your model,customers, should now build as a view.- BigQuery users need to run
dbt run --full-refreshinstead ofdbt runto full apply materialization changes.
- BigQuery users need to run
-
Enter the
dbt run --full-refreshcommand for this to take effect in your warehouse.
FAQs
Delete the example models
You can now delete the files that dbt created when you initialized the project:
-
Delete the
models/example/directory. -
Delete the
example:key from yourdbt_project.ymlfile, and any configurations that are listed under it.dbt_project.yml# before
models:
jaffle_shop:
+materialized: table
example:
+materialized: viewdbt_project.yml# after
models:
jaffle_shop:
+materialized: table -
Save your changes.
FAQs
Build models on top of other models
As a best practice in SQL, you should separate logic that cleans up your data from logic that transforms your data. You have already started doing this in the existing query by using common table expressions (CTEs).
Now you can experiment by separating the logic out into separate models and using the ref function to build models on top of other models:
-
Create a new SQL file,
models/stg_customers.sql, with the SQL from thecustomersCTE in our original query. -
Create a second new SQL file,
models/stg_orders.sql, with the SQL from theordersCTE in our original query.models/stg_customers.sqlselect
id as customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
from `dbt-tutorial`.jaffle_shop.customersmodels/stg_orders.sqlselect
id as order_id,
user_id as customer_id,
order_date,
status
from `dbt-tutorial`.jaffle_shop.orders -
Edit the SQL in your
models/customers.sqlfile as follows:models/customers.sqlwith customers as (
select * from {{ ref('stg_customers') }}
),
orders as (
select * from {{ ref('stg_orders') }}
),
customer_orders as (
select
customer_id,
min(order_date) as first_order_date,
max(order_date) as most_recent_order_date,
count(order_id) as number_of_orders
from orders
group by 1
),
final as (
select
customers.customer_id,
customers.first_name,
customers.last_name,
customer_orders.first_order_date,
customer_orders.most_recent_order_date,
coalesce(customer_orders.number_of_orders, 0) as number_of_orders
from customers
left join customer_orders using (customer_id)
)
select * from final -
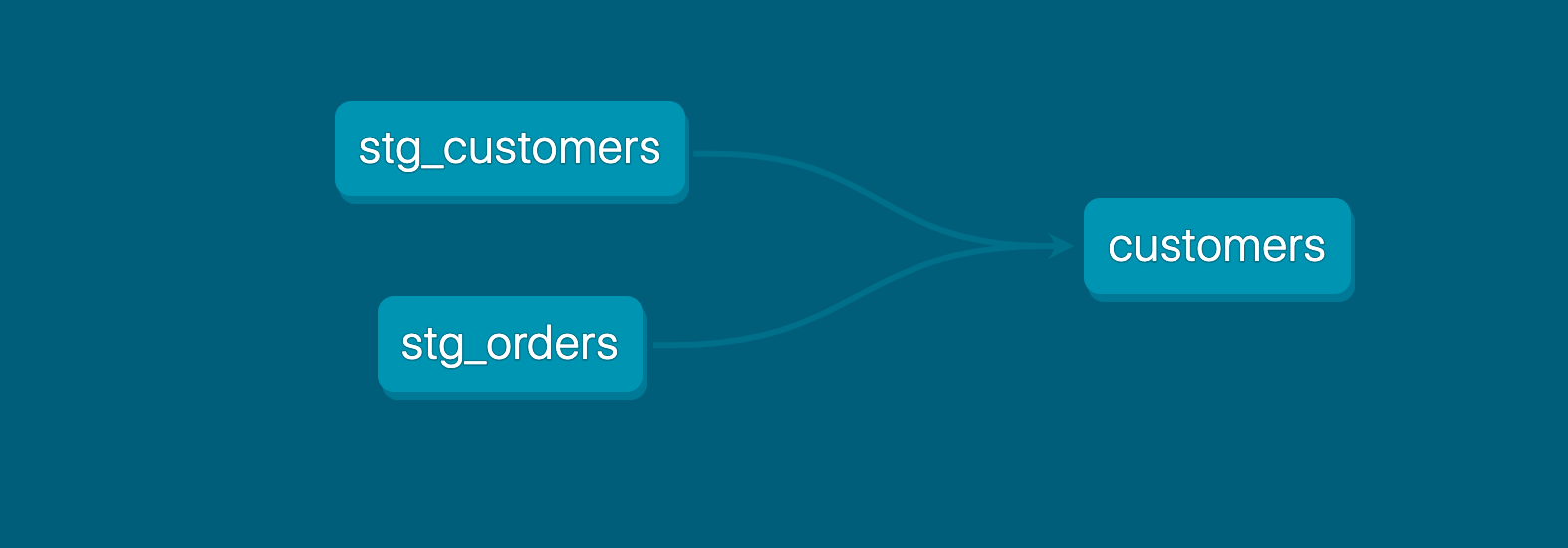
Execute
dbt run.This time, when you performed a
dbt run, separate views/tables were created forstg_customers,stg_ordersandcustomers. dbt inferred the order to run these models. Becausecustomersdepends onstg_customersandstg_orders, dbt buildscustomerslast. You do not need to explicitly define these dependencies.
Build models on top of sources
Sources make it possible to name and describe the data loaded into your warehouse by your extract and load tools. By declaring these tables as sources in dbt, you can:
- select from source tables in your models using the
{{ source() }}function, helping define the lineage of your data - test your assumptions about your source data
- calculate the freshness of your source data
-
Create a new YML file
models/sources.yml. -
Declare the sources by copying the following into the file and clicking Save.
models/sources.yml
sources:
- name: jaffle_shop
description: This is a replica of the Postgres database used by our app
database: dbt-tutorial
schema: jaffle_shop
tables:
- name: customers
description: One record per customer.
- name: orders
description: One record per order. Includes cancelled and deleted orders. -
Edit the
models/stg_customers.sqlfile to select from thecustomerstable in thejaffle_shopsource.models/stg_customers.sqlselect
id as customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
from {{ source('jaffle_shop', 'customers') }} -
Edit the
models/stg_orders.sqlfile to select from theorderstable in thejaffle_shopsource.models/stg_orders.sqlselect
id as order_id,
user_id as customer_id,
order_date,
status
from {{ source('jaffle_shop', 'orders') }} -
Execute
dbt run.The results of your
dbt runwill be exactly the same as the previous step. Yourstg_customersandstg_ordersmodels will still query from the same raw data source in BigQuery. By usingsource, you can test and document your raw data and also understand the lineage of your sources.
FAQs
Add tests to your models
Adding data tests to a project helps validate that your models are working correctly.
To add data tests to your project:
-
Create a new YAML file in the
modelsdirectory, namedmodels/schema.yml -
Add the following contents to the file:
models/schema.ymlversion: 2
models:
- name: customers
columns:
- name: customer_id
data_tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: stg_customers
columns:
- name: customer_id
data_tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: stg_orders
columns:
- name: order_id
data_tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: status
data_tests:
- accepted_values:
arguments: # available in v1.10.5 and higher. Older versions can set the <argument_name> as the top-level property.
values: ['placed', 'shipped', 'completed', 'return_pending', 'returned']
- name: customer_id
data_tests:
- not_null
- relationships:
arguments:
to: ref('stg_customers')
field: customer_id -
Run
dbt test, and confirm that all your tests passed.
When you run dbt test, dbt iterates through your YAML files, and constructs a query for each test. Each query will return the number of records that fail the test. If this number is 0, then the test is successful.
FAQs
Document your models
Adding documentation to your project allows you to describe your models in rich detail, and share that information with your team. Here, we're going to add some basic documentation to our project.
Update your models/schema.yml file to include some descriptions, such as those below.
version: 2
models:
- name: customers
description: One record per customer
columns:
- name: customer_id
description: Primary key
data_tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: first_order_date
description: NULL when a customer has not yet placed an order.
- name: stg_customers
description: This model cleans up customer data
columns:
- name: customer_id
description: Primary key
data_tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: stg_orders
description: This model cleans up order data
columns:
- name: order_id
description: Primary key
data_tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: status
data_tests:
- accepted_values:
arguments: # available in v1.10.5 and higher. Older versions can set the <argument_name> as the top-level property.
values: ['placed', 'shipped', 'completed', 'return_pending', 'returned']
- name: customer_id
data_tests:
- not_null
- relationships:
arguments:
to: ref('stg_customers')
field: customer_id
- View in Catalog
- View in Studio IDE
Catalog provides powerful tools to interact with your dbt projects, including documentation:
- From the IDE, run one of the following commands:
dbt docs generateif you're on dbt Coredbt buildif you're on the dbt Fusion engine
- Click Catalog in the navigation menu to launch Catalog.
- In the Catalog pane, click the environment selection dropdown menu at the top of the file tree and change it from Production to Development.
- Select your project from the file tree.
- Use the search bar or browse the resource list to find the
customersmodel. - Click the model to view its details, including the descriptions you added.
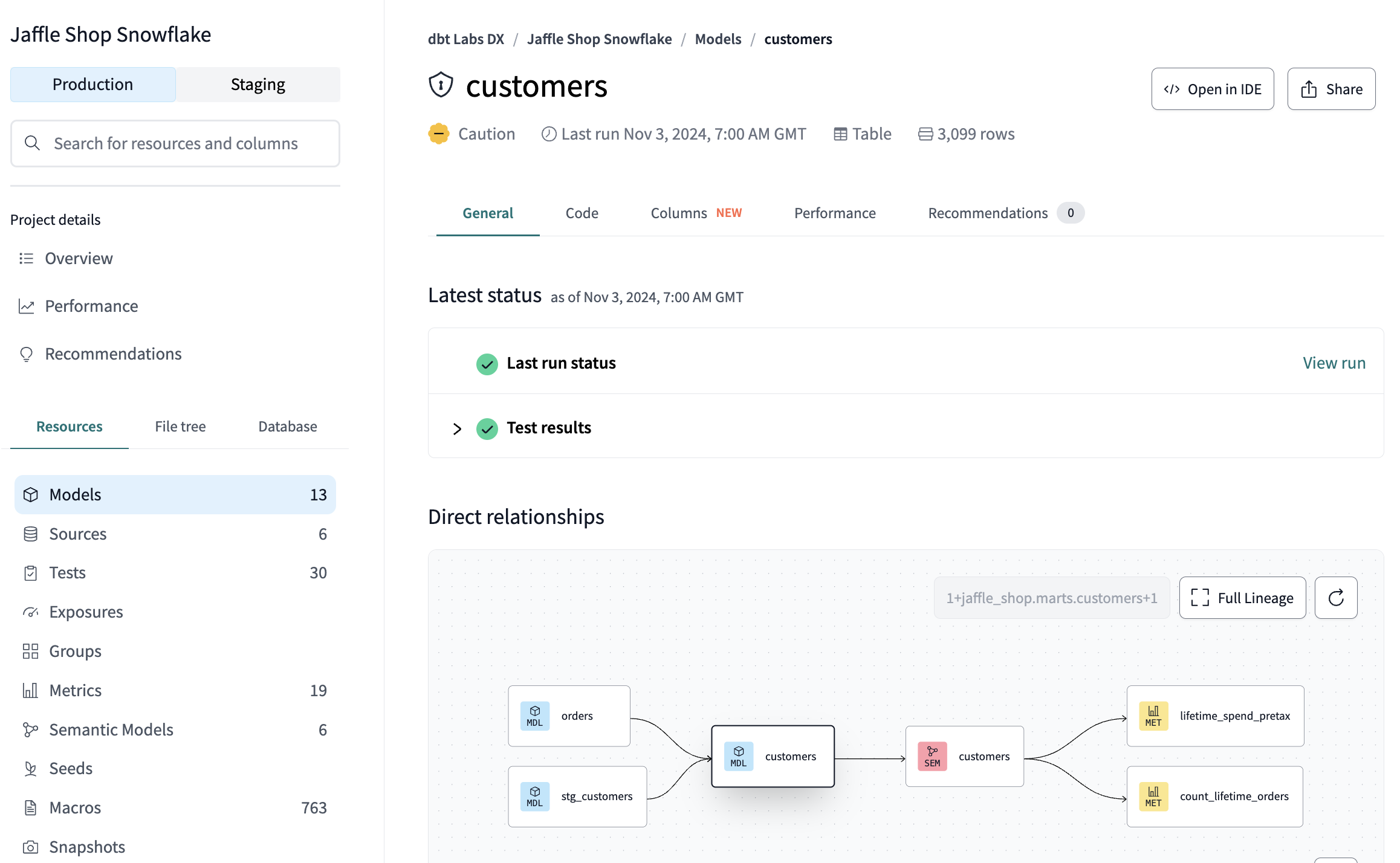
Catalog displays your model's description, column documentation, data tests, and lineage graph. You can also see which columns are missing documentation and track test coverage across your project.
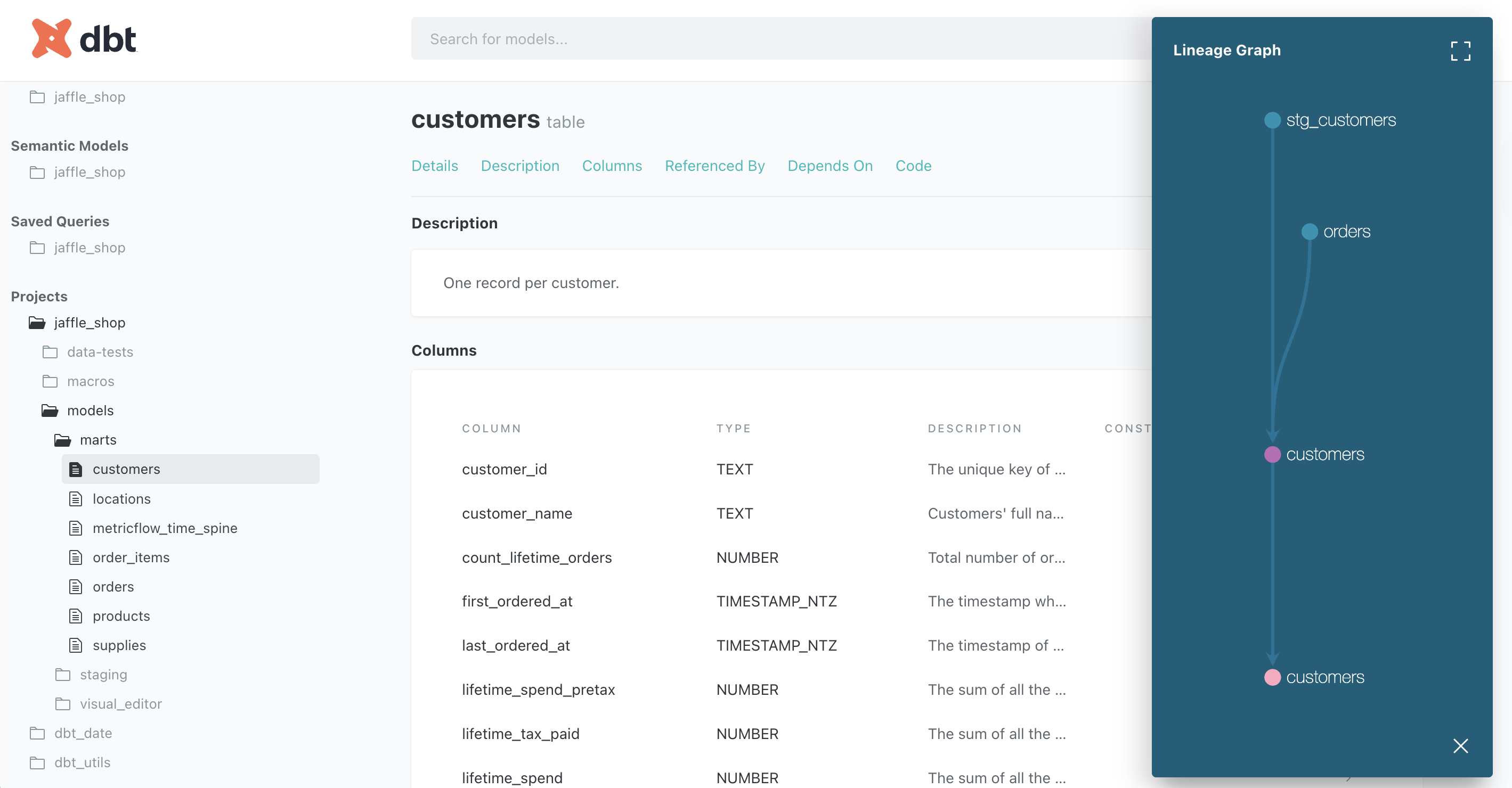
You can view docs directly from the IDE if you're on Latest or another version of dbt Core. Keep in mind that this is a legacy view and doesn't offer the same level of interactivity as Catalog.
- In the IDE, run
dbt docs generate. - From the navigation bar, click the View docs icon located to the right of the branch name.
- From Projects, select your project name and expand the folders.
- Click models > marts > customers.
FAQs
Commit your changes
Now that you've built your customer model, you need to commit the changes you made to the project so that the repository has your latest code.
If you edited directly in the protected primary branch:
- Click the Commit and sync git button. This action prepares your changes for commit.
- A modal titled Commit to a new branch will appear.
- In the modal window, name your new branch
add-customers-model. This branches off from your primary branch with your new changes. - Add a commit message, such as "Add customers model, tests, docs" and and commit your changes.
- Click Merge this branch to main to add these changes to the main branch on your repo.
If you created a new branch before editing:
- Since you already branched out of the primary protected branch, go to Version Control on the left.
- Click Commit and sync to add a message.
- Add a commit message, such as "Add customers model, tests, docs."
- Click Merge this branch to main to add these changes to the main branch on your repo.
Deploy dbt
Use dbt's Scheduler to deploy your production jobs confidently and build observability into your processes. You'll learn to create a deployment environment and run a job in the following steps.
Create a deployment environment
- From the main menu, go to Orchestration > Environments.
- Click Create environment.
- In the Name field, write the name of your deployment environment. For example, "Production."
- The dbt version will default to the latest available. We recommend all new projects run on the latest version of dbt.
- Under Deployment connection, enter the name of the dataset you want to use as the target, such as "Analytics". This will allow dbt to build and work with that dataset. For some data warehouses, the target dataset may be referred to as a "schema".
- Click Save.
Create and run a job
Jobs are a set of dbt commands that you want to run on a schedule. For example, dbt build.
As the jaffle_shop business gains more customers, and those customers create more orders, you will see more records added to your source data. Because you materialized the customers model as a table, you'll need to periodically rebuild your table to ensure that the data stays up-to-date. This update will happen when you run a job.
- After creating your deployment environment, you should be directed to the page for a new environment. If not, select Orchestration from the main menu, then click Jobs.
- Click Create job > Deploy job.
- Provide a job name (for example, "Production run") and select the environment you just created.
- Scroll down to the Execution settings section.
- Under Commands, add this command as part of your job if you don't see it:
dbt build
- Select the Generate docs on run option to automatically generate updated project docs each time your job runs.
- For this exercise, do not set a schedule for your project to run — while your organization's project should run regularly, there's no need to run this example project on a schedule. Scheduling a job is sometimes referred to as deploying a project.
- Click Save, then click Run now to run your job.
- Click the run and watch its progress under Run summary.
- Once the run is complete, click View Documentation to see the docs for your project.
Congratulations 🎉! You've just deployed your first dbt project!
FAQs
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.