persist_docs
- Models
- Sources
- Seeds
- Snapshots
models:
<resource-path>:
+persist_docs:
relation: true
columns: true
{{ config(
persist_docs={"relation": true, "columns": true}
) }}
select ...
This config is not implemented for sources.
seeds:
<resource-path>:
+persist_docs:
relation: true
columns: true
snapshots:
<resource-path>:
+persist_docs:
relation: true
columns: true
{% snapshot snapshot_name %}
{{ config(
persist_docs={"relation": true, "columns": true}
) }}
select ...
{% endsnapshot %}
Definition
Optionally persist resource descriptions as column and relation comments in the database. By default, documentation persistence is disabled, but it can be enabled for specific resources or groups of resources as needed.
Support
The persist_docs config is supported on the most widely used dbt adapters:
- Postgres
- Redshift
- Snowflake
- BigQuery
- Databricks
- Apache Spark
However, some databases limit where and how descriptions can be added to database objects. Those database adapters might not support persist_docs, or might offer only partial support.
Some known issues and limitations:
- Databricks
- Snowflake
- Column-level comments require
file_format: delta(or another "v2 file format").
-
If a column name in a SQL model is in a mixed-case format (for example,
ca_net_ht_N), the docs for that column will not be persisted. For the docs to persist, there are two options:- Define the column name in the corresponding YML file using lowercase or uppercase letters only.
- Use the
quoteconfiguration in the corresponding YML file.
See the following sample steps on how to use the
quotefield for columns in a mixed-case format.-
Create the following SQL and YML files:
<modelname>.sql{{ config(materialized='table') }}
select 1 as "ca_net_ht_N" # note the use of double quotes for the column name<modelname>.ymlmodels:
- name: <modelname>
description: This is the table description
columns:
- name: "ca_net_ht_N"
description: This should be the description of the column
quote: true -
Run
dbt build -s models/<modelname>.sql --full-refresh. -
Open the logs at
logs/dbt.logand check the column description:alter table analytics.<schema>.<modelname> alter
"ca_net_ht_N" COMMENT $$This should be the description of the column$$;
Usage
Documenting columns and relations
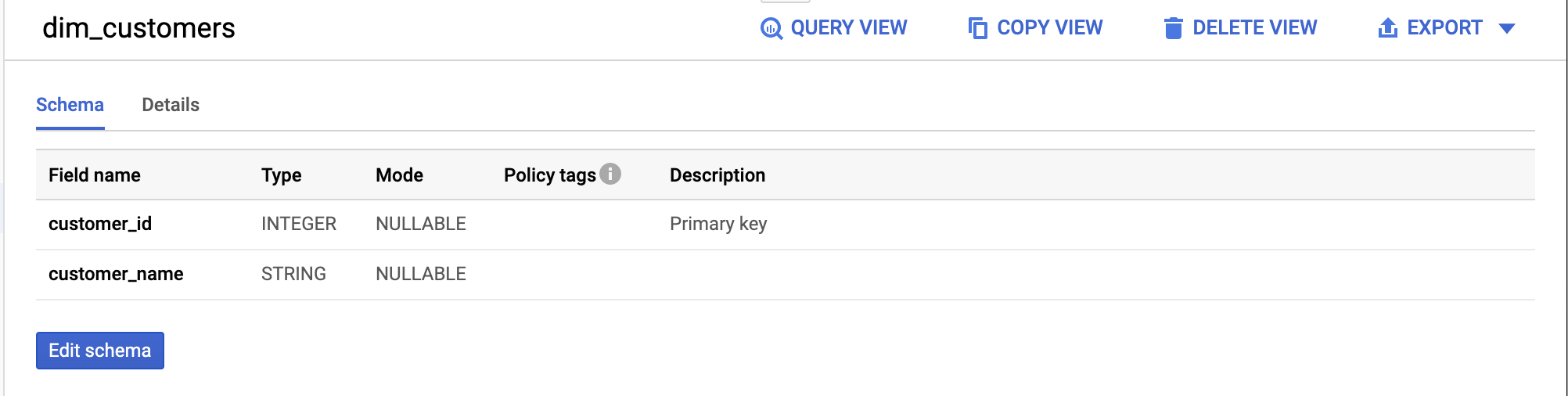
Supply a description for a model:
models:
- name: dim_customers
description: One record per customer
columns:
- name: customer_id
description: Primary key
Enable persist_docs for columns and relations in your project:
models:
+persist_docs:
relation: true
columns: true
Run dbt and observe that the created relation and columns are annotated with your descriptions:
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.