Node selector methods
Selector methods return all resources that share a common property, using the
syntax method:value. While it is recommended to explicitly denote the method,
you can omit it (the default value will be one of path, file or fqn).
You can combine multiple selector methods in one --select command by separating them with commas (,) without whitespace (for example, dbt run --select "marts.finance,tag:nightly"). This only selects resources that satisfy all arguments. In this example, the command runs models that are in the marts/finance subdirectory and tagged nightly. For more information, see Set operators.
Many of the methods below support Unix-style wildcards:
| Loading table... |
For example:
dbt list --select "*.folder_name.*"
dbt list --select "package:*_source"
access
The access method selects models based on their access property.
dbt list --select "access:public" # list all public models
dbt list --select "access:private" # list all private models
dbt list --select "access:protected" # list all protected models
config
The config method is used to select models that match a specified node config.
dbt run --select "config.materialized:incremental" # run all models that are materialized incrementally
dbt run --select "config.schema:audit" # run all models that are created in the `audit` schema
dbt run --select "config.cluster_by:geo_country" # run all models clustered by `geo_country`
While most config values are strings, you can also use the config method to match boolean configs, dictionary keys, and values in lists.
For example, given a model with the following configurations:
{{ config(
materialized = 'incremental',
unique_key = ['column_a', 'column_b'],
grants = {'select': ['reporter', 'analysts']},
meta = {"contains_pii": true},
transient = true
) }}
select ...
You can select using any of the following:
dbt ls -s config.materialized:incremental
dbt ls -s config.unique_key:column_a
dbt ls -s config.grants.select:reporter
dbt ls -s config.meta.contains_pii:true
dbt ls -s config.transient:true
exposure
The exposure method is used to select parent resources of a specified exposure. Use in conjunction with the + operator.
dbt run --select "+exposure:weekly_kpis" # run all models that feed into the weekly_kpis exposure
dbt test --select "+exposure:*" # test all resources upstream of all exposures
dbt ls --select "+exposure:*" --resource-type source # list all source tables upstream of all exposures
file
fqn
The fqn method is used to select nodes based off their "fully qualified names" (FQN) within the dbt graph. The default output of dbt list is a listing of FQN. The default FQN format is composed of the project name, subdirectories within the path, and the file name (without extension) separated by periods.
dbt run --select "fqn:some_model"
dbt run --select "fqn:your_project.some_model"
dbt run --select "fqn:some_package.some_other_model"
dbt run --select "fqn:some_path.some_model"
dbt run --select "fqn:your_project.some_path.some_model"
group
The group method is used to select models defined within a group.
dbt run --select "group:finance" # run all models that belong to the finance group.
metric
The metric method is used to select parent resources of a specified metric. Use in conjunction with the + operator.
dbt build --select "+metric:weekly_active_users" # build all resources upstream of weekly_active_users metric
dbt ls --select "+metric:*" --resource-type source # list all source tables upstream of all metrics
package
The package method is used to select models defined within the root project
or an installed dbt package. While the package: prefix is not explicitly required, it may be used to make
selectors unambiguous.
# These three selectors are equivalent
dbt run --select "package:snowplow"
dbt run --select "snowplow"
dbt run --select "snowplow.*"
Use the this package to select nodes from the current project. From the example, running dbt run --select "package:this" from the snowplow project runs the exact same set of models as the other three selectors.
Since this always refers to the current project, using package:this ensures that you're only selecting models from the project you're working in.
path
resource_type
result
The result method is related to the state method and can be used to select resources based on their result status from a prior run. Note that one of the dbt commands [run, test, build, seed] must have been performed in order to create the result on which a result selector operates.
You can use result selectors in conjunction with the + operator.
# run all models that generated errors on the prior invocation of dbt run
dbt run --select "result:error" --state path/to/artifacts
# run all tests that failed on the prior invocation of dbt test
dbt test --select "result:fail" --state path/to/artifacts
# run all the models associated with failed tests from the prior invocation of dbt build
dbt build --select "1+result:fail" --state path/to/artifacts
# run all seeds that generated errors on the prior invocation of dbt seed
dbt seed --select "result:error" --state path/to/artifacts
- Only use
result:failwhen you want to re-run tests that failed during the last invocation. This selector is specific to test nodes. Tests don't have downstream nodes in the DAG, so using theresult:fail+selector will only return the failed test itself and not the model or anything built on top of it. - On the other hand,
result:errorselects any resource (models, tests, snapshots, and more) that returned an error. - As an example, to re-run upstream and downstream resources associated with failed tests, you can use one of the following selectors:
# reruns all the models associated with failed tests from the prior invocation of dbt build
dbt build --select "1+result:fail" --state path/to/artifacts
# reruns the models associated with failed tests and all downstream dependencies - especially useful in deferred state workflows
dbt build --select "1+result:fail+" --state path/to/artifacts
saved_query
The saved_query method selects saved queries.
dbt list --select "saved_query:*" # list all saved queries
dbt list --select "+saved_query:orders_saved_query" # list your saved query named "orders_saved_query" and all upstream resources
semantic_model
The semantic_model method selects semantic models.
dbt list --select "semantic_model:*" # list all semantic models
dbt list --select "+semantic_model:orders" # list your semantic model named "orders" and all upstream resources
source
The source method is used to select models that select from a specified source. Use in conjunction with the + operator.
dbt run --select "source:snowplow+" # run all models that select from Snowplow sources
dbt run --select "source:snowplow.events+" # run all models downstream of the events table in the Snowplow source
Refer to source FAQs for more info.
source_status
Another element of job state is the source_status of a prior dbt invocation. After executing dbt source freshness, for example, dbt creates the sources.json artifact which contains execution times and max_loaded_at dates for dbt sources. You can read more about sources.json on the 'sources' page.
The following dbt commands produce sources.json artifacts whose results can be referenced in subsequent dbt invocations:
dbt source freshness
After issuing one of the above commands, you can reference the source freshness results by adding a selector to a subsequent command as follows:
# You can also set the DBT_STATE environment variable instead of the --state flag.
dbt source freshness # must be run again to compare current to previous state
dbt build --select "source_status:fresher+" --state path/to/prod/artifacts
state
N.B. State-based selection is a powerful, complex feature. Read about known caveats and limitations to state comparison.
The state method is used to select nodes by comparing them against a previous version of the same project, which is represented by a manifest. The file path of the comparison manifest must be specified via the --state flag or DBT_STATE environment variable.
state:new: There is no node with the same unique_id in the comparison manifest
state:modified: All new nodes, plus any changes to existing nodes.
dbt test --select "state:new" --state path/to/artifacts # run all tests on new models + and new tests on old models
dbt run --select "state:modified" --state path/to/artifacts # run all models that have been modified
dbt ls --select "state:modified" --state path/to/artifacts # list all modified nodes (not just models)
Because state comparison is complex, and everyone's project is different, dbt supports subselectors that include a subset of the full modified criteria:
state:modified.body: Changes to node body (e.g. model SQL, seed values)state:modified.configs: Changes to any node configs, excludingdatabase/schema/aliasstate:modified.relation: Changes todatabase/schema/alias(the database representation of this node), irrespective oftargetvalues orgenerate_x_namemacrosstate:modified.persisted_descriptions: Changes to relation- or column-leveldescription, if and only ifpersist_docsis enabled at each levelstate:modified.macros: Changes to upstream macros (whether called directly or indirectly by another macro)state:modified.contract: Changes to a model's contract, which currently include thenameanddata_typeofcolumns. Removing or changing the type of an existing column is considered a breaking change, and will raise an error.
Remember that state:modified includes all of the criteria above, as well as some extra resource-specific criteria, such as modifying a source's freshness or quoting rules or an exposure's maturity property. (View the source code for the full set of checks used when comparing sources, exposures, and executable nodes.)
There are two additional state selectors that complement state:new and state:modified by representing the inverse of those functions:
state:old— A node with the sameunique_idexists in the comparison manifeststate:unmodified— All existing nodes with no changes
These selectors can help you shorten run times by excluding unchanged nodes. Currently, no subselectors are available at this time, but that might change as use cases evolve.
state:modified node and reference impacts
state:modified identifies any new nodes added, changes to existing nodes, and any changes made to:
- access permissions
deprecation_datelatest_version
If a node changes its group, downstream references may break, potentially causing build failures.
As group is a config, and configs are generally included in state:modified detection, modifying the group name everywhere it's referenced will flag those nodes as "modified".
Depending on whether partial parsing is enabled, you will catch the breakage as part of CI workflows.
- If you change a group name everywhere it's referenced, and partial parsing is enabled, dbt may only re-parse the changed model.
- If you update a group name in all its references without partial parsing enabled, dbt will re-parse all models and identify any invalid downstream references.
An error along the lines of "there's nothing to do" can occur when you change the group name and something is picked up to be run via dbt build --select state:modified. This error will be caught at runtime so long as the CI job is selecting state:modified+ (including downstreams).
Certain factors can affect how references are used or resolved later on, including:
- Modifying access: if permissions or access rules change, some references might stop working.
- Modifying
deprecation_date: if a reference or model version is marked deprecated, new warnings might appear that affect how references are processed. - Modifying
latest_version: if there's no tie to a specific version, the reference or model will point to the latest version.- If a newer version is released, the reference will automatically resolve to the new version, potentially changing the behavior or output of the system that relies on it.
dbt handles state comparison for seed files differently depending on their size:
- Seed files smaller than 1 MiB — Included in the
state:modifiedselector only when the contents change. - Seed files 1 MiB or larger — Included in the
state:modifiedselector only when the seed file path changes.
Overwrites the manifest.json
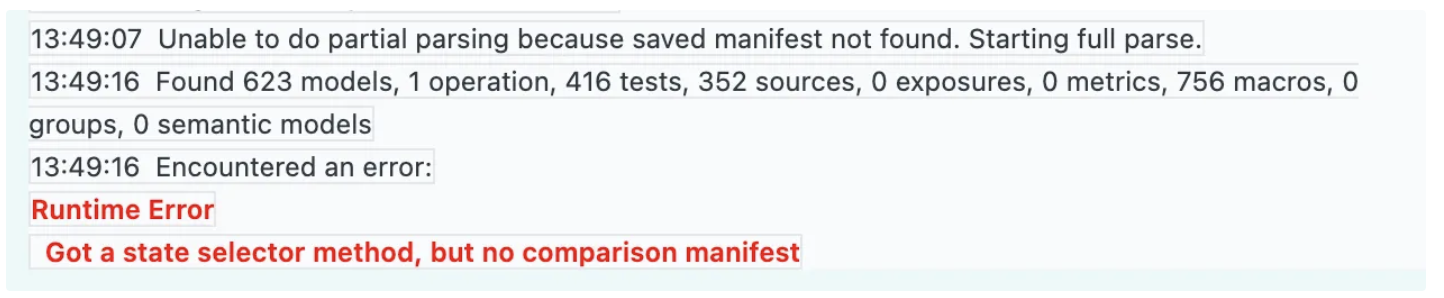
dbt overwrites the manifest.json file during parsing, which means when you reference --state from the target/ directory, you may encounter a warning indicating that the saved manifest wasn't found.
During the next job run, dbt follows a sequence of steps that lead to the issue. First, it overwrites target/manifest.json before it can be used for change detection. Then, when dbt tries to read target/manifest.json again to detect changes, it finds none because the previous state has already been overwritten/erased.
Avoid setting --state and --target-path to the same path with state-dependent features like --defer and state:modified as it can lead to non-idempotent behavior and won't work as expected.
Recommendation
To prevent the manifest.json from being overwritten before dbt reads it for change detection, update your workflow using one of these methods:
-
Move the
manifest.jsonto a dedicated folder (for examplestate/) after dbt generates it in thetarget/ folder. This makes sure dbt references the correct saved state instead of comparing the current state with the just-overwritten version. It also avoids issues caused by setting--stateand--target-pathto the same location, which can lead to non-idempotent behavior. -
Write the manifest to a different
--target-pathin the build stage (where dbt would generate thetarget/manifest.json) or before it gets overwritten during job execution to avoid issues with change detection. This allows dbt to detect changes instead of comparing the current state with the just-overwritten version. -
Pass the
--no-write-jsonflag:dbt ls --no-write-json --select state:modified --state target: during the reproduction stage.
tag
The tag: method is used to select models that match a specified tag.
dbt run --select "tag:nightly" # run all models with the `nightly` tag
test_name
The test_name method is used to select tests based on the name of the generic test
that defines it. For more information about how generic tests are defined, read about
data tests.
dbt test --select "test_name:unique" # run all instances of the `unique` test
dbt test --select "test_name:equality" # run all instances of the `dbt_utils.equality` test
dbt test --select "test_name:range_min_max" # run all instances of a custom schema test defined in the local project, `range_min_max`
The test_type
The test_type method is used to select tests based on their type:
dbt test --select "test_type:unit" # run all unit tests
dbt test --select "test_type:data" # run all data tests
dbt test --select "test_type:generic" # run all generic data tests
dbt test --select "test_type:singular" # run all singular data tests
unit_test
The unit_test method selects unit tests.
dbt list --select "unit_test:*" # list all unit tests
dbt list --select "+unit_test:orders_with_zero_items" # list your unit test named "orders_with_zero_items" and all upstream resources
version
The version method selects versioned models based on their version identifier and latest version.
dbt list --select "version:latest" # only 'latest' versions
dbt list --select "version:prerelease" # versions newer than the 'latest' version
dbt list --select "version:old" # versions older than the 'latest' version
dbt list --select "version:none" # models that are *not* versioned
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.