About state-aware orchestration Private previewEnterpriseEnterprise +
Every time a job runs, state-aware orchestration automatically determines which models to build by detecting changes in code or data.
The dbt Fusion Engine is currently available for installation in:
- Local command line interface (CLI) tools Preview
- VS Code and Cursor with the dbt extension Preview
- dbt platform environments Private preview
Join the conversation in our Community Slack channel #dbt-fusion-engine.
Read the Fusion Diaries for the latest updates.
State-aware orchestration saves you compute costs and reduces runtime because when a job runs, it checks for new records and only builds the models that will change.
We built dbt's state-aware orchestration on these four core principles:
- Real-time shared state: All jobs write to a real-time shared model-level state, allowing dbt to rebuild only changed models regardless of which jobs the model is built in.
- Model-level queueing: Jobs queue up at the model-level so you can avoid any 'collisions' and prevent rebuilding models that were just updated by another job.
- State-aware and state agnostic support: You can build jobs dynamically (state-aware) or explicitly (state-agnostic). Both approaches update shared state so everything is kept in sync.
- Sensible defaults: State-aware orchestration works out-of-the-box (natively), with an optional configuration setting for more advanced controls. For more information, refer to state-aware advanced configurations.
Optimizing builds with state-aware orchestration
State-aware orchestration uses shared state tracking to determine which models need to be built by detecting changes in code or data every time a job runs. It also supports custom refresh intervals and custom source freshness configurations, so dbt only rebuilds models when they're actually needed.
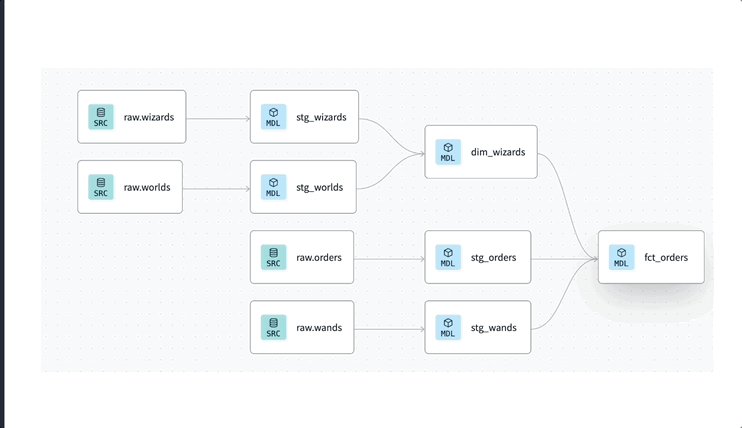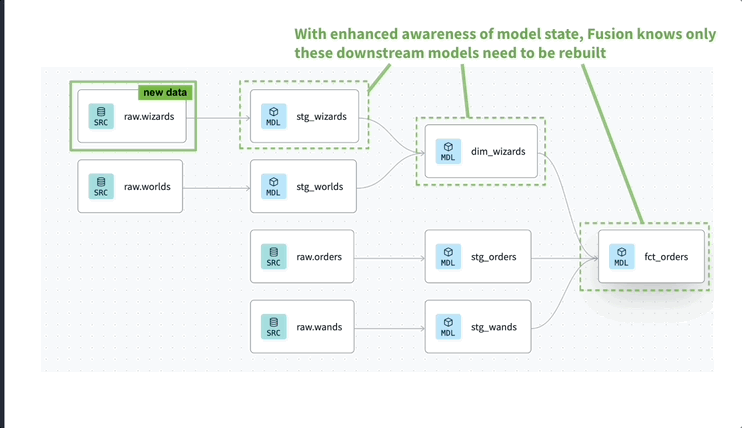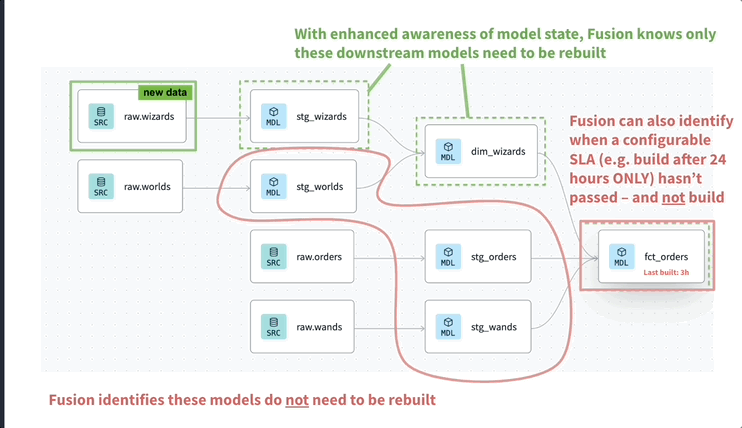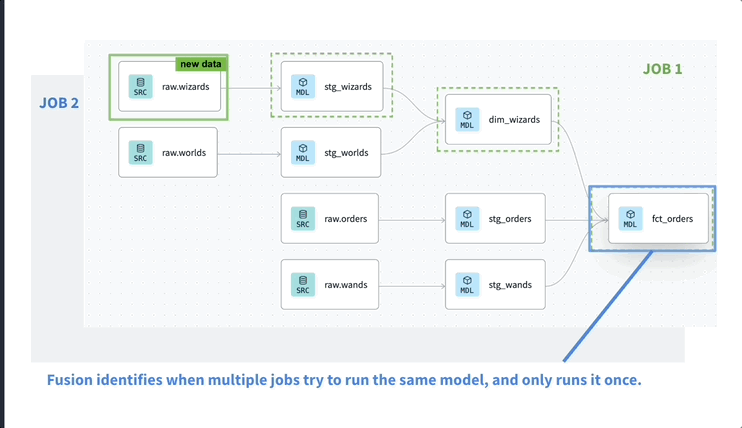
For example, you can configure your project so that dbt skips rebuilding the dim_wizards model (and its parents) if they’ve already been refreshed within the last 4 hours, even if the job itself runs more frequently.
Without configuring anything, dbt's state-aware orchestration automatically knows to build your models either when the code has changed or if there’s any new data in a source (or upstream model in the case of dbt Mesh).
Efficient Testing in state-aware orchestration Private beta
State-aware orchestration features in the dbt platform are only available in Fusion, which is in private preview. Contact your account manager to enable Fusion in your account.
Data quality can get degraded in two ways:
- New code changes definitions or introduces edge cases.
- New data, like duplicates or unexpected values, invalidates downstream metrics.
Running dbt’s out-of-the-box data tests (unique, not_null, accepted_values, relationships) on every build helps catch data errors before they impact business decisions. Catching these errors often requires having multiple tests on every model and running tests even when not necessary. If nothing relevant has changed, repeated test executions don’t improve coverage and only increase cost.
With Fusion, dbt gains an understanding of the SQL code based on the logical plan for the compiled code. dbt then can determine when a test must run again, or when a prior upstream test result can be reused.
Efficient Testing in state-aware orchestration reduces warehouse costs by avoiding redundant data tests and combining multiple tests into one run. This feature includes two optimizations:
- Test reuse — Tests are reused in cases where no logic in the code or no new data could have changed the test's outcome.
- Test aggregation — When there are multiple tests on a model, dbt combines tests to run as a single query against the warehouse, rather than running separate queries for each test.
Supported data tests
The following tests can be reused when Efficient Testing is enabled:
Enabling Efficient Testing
To enable Efficient Testing:
- From the main menu, go to Orchestration > Jobs.
- Select your job. Go to your job settings and click Edit.
- Under Enable Fusion cost optimization features, expand More options.
- Select Efficient Testing. This feature is disabled by default.
- Click Save.
Example
In the following query, you’re joining an orders and a customers table:
with
orders as (select * from ref('orders')),
customers as (select * from ref('customers')),
joined as (
select
customers.customer_id as customer_id,
orders.order_id as order_id
from customers
left join orders
on orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id
)
select * from joined
-
not_nulltest: Aleft joincan introduce null values for customers without orders. Even if upstream tests verifiednot_null(order_id)in orders, the join can create null values downstream. dbt must always run anot_nulltest onorder_idin this joined result. -
uniquetest: Iforders.order_idandcustomers.customer_idare unique upstream, uniqueness oforder_idis preserved and the upstream result can be reused.
Limitation
The following section lists some considerations when using Efficient Testing in state-aware-orchestration:
-
Aggregated tests do not support custom configs. Tests that include the following custom config options will run individually rather than as part of the aggregated batch:
config:
fail_calc: <string>
limit: <integer>
severity: error | warn
error_if: <string>
warn_if: <string>
store_failures: true | false
where: <string>
Related docs
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.