Configuring Snowflake PrivateLink Enterprise +
The private connection feature is available on the following dbt Enterprise tiers:
- Business Critical
- Virtual Private
To learn more about these tiers, contact us at sales@getdbt.com.
The following steps walk you through the setup of an AWS-hosted Snowflake PrivateLink endpoint in a dbt multi-tenant environment.
Private connection endpoints can't connect across cloud providers (AWS, Azure, and GCP). For a private connection to work, both dbt and the server (like Snowflake) must be hosted on the same cloud provider. For example, dbt hosted on AWS cannot connect to services hosted on Azure, and dbt hosted on Azure can’t connect to services hosted on GCP.
Users connecting to Snowflake using Snowflake OAuth over an AWS PrivateLink connection from dbt will also require access to a PrivateLink endpoint from their local workstation. Where possible, use Snowflake External OAuth instead to bypass this limitation.
From the Snowflake docs:
Currently, for any given Snowflake account, SSO works with only one account URL at a time: either the public account URL or the URL associated with the private connectivity service
Configure AWS PrivateLink
To configure Snowflake instances hosted on AWS for PrivateLink:
- Open a support case with Snowflake to allow access from the dbt AWS account.
- Snowflake prefers that the account owner opens the support case directly rather than dbt Labs acting on their behalf. For more information, refer to Snowflake's knowledge base article.
- Provide them with your dbt account ID along with any other information requested in the article.
- AWS account ID:
346425330055— Note: This account ID only applies to AWS dbt multi-tenant environments. For AWS Virtual Private/Single-Tenant account IDs, contact dbt Support.
- AWS account ID:
- You need
ACCOUNTADMINaccess to the Snowflake instance to submit a support request.
-
After Snowflake has granted the requested access, run the Snowflake system function SYSTEM$GET_PRIVATELINK_CONFIG and copy the output.
-
Add the required information to the following template and submit your request to dbt Support:
Subject: New Multi-Tenant (Azure or AWS) PrivateLink Request
- Type: Snowflake
- SYSTEM$GET_PRIVATELINK_CONFIG output:
- *Use privatelink-account-url or regionless-privatelink-account-url?:
- **Create Internal Stage PrivateLink endpoint? (Y/N):
- dbt AWS multi-tenant environment (US, EMEA, AU):
*By default, dbt will be configured to use privatelink-account-url from the provided SYSTEM$GET_PRIVATELINK_CONFIG as the PrivateLink endpoint. Upon request, regionless-privatelink-account-url can be used instead.
** Internal Stage PrivateLink must be enabled on the Snowflake account to use this feature
dbt Labs will work on your behalf to complete the private connection setup. Please allow 3-5 business days for this process to complete. Support will contact you when the endpoint is available.
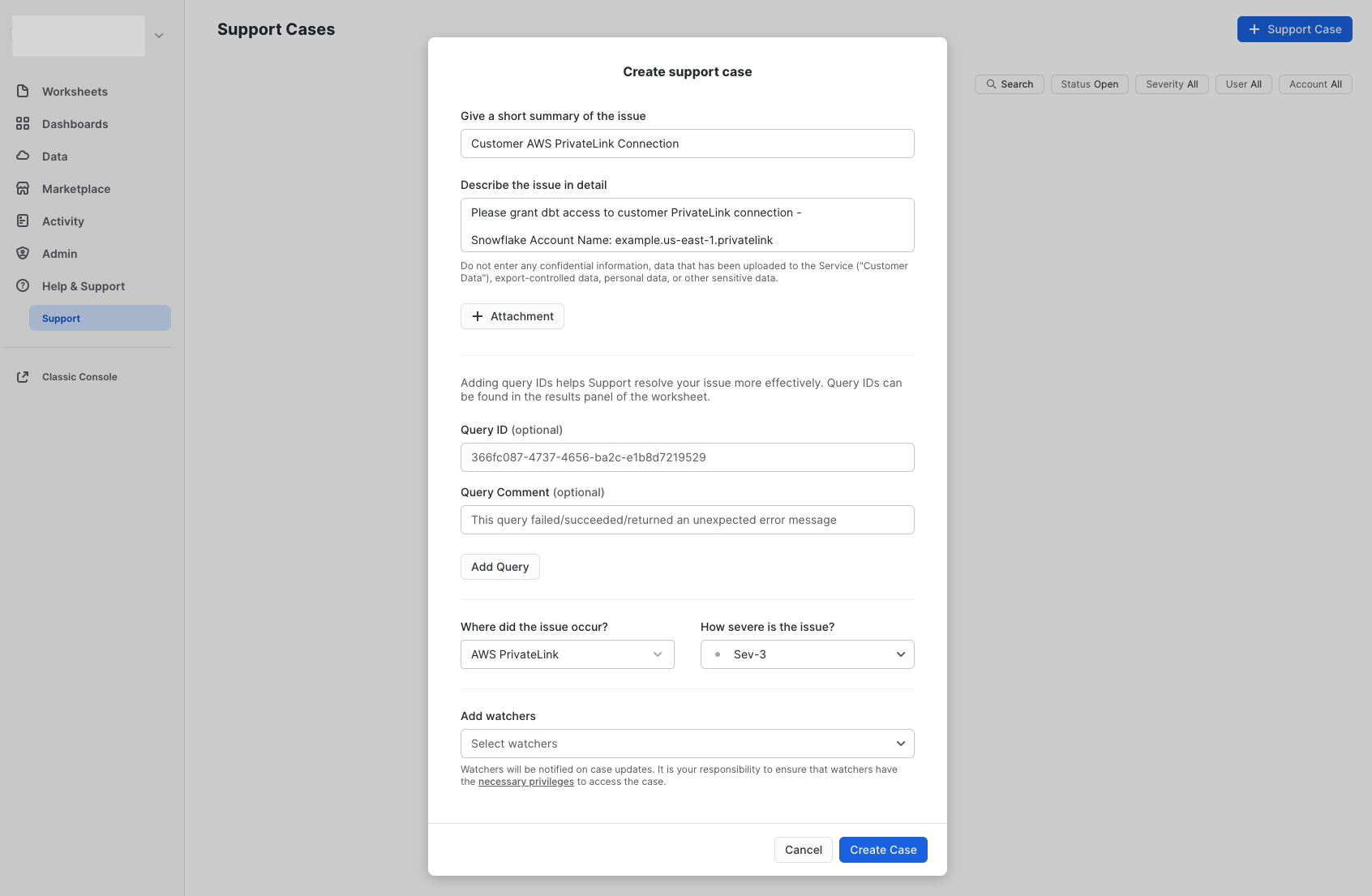
Create connection in dbt
Once dbt Support completes the configuration, you can start creating new connections using PrivateLink.
- Navigate to Settings → Create new project → select Snowflake.
- You will see two radio buttons: Public and Private. Select Private.
- Select the private endpoint from the dropdown (this automatically populates the hostname/account field).
- Configure the remaining data platform details.
- Test your connection and save it.
Configuring internal stage PrivateLink in dbt
If an Internal Stage PrivateLink endpoint has been provisioned, your dbt environments must be configured to use this endpoint instead of the account default set in Snowflake.
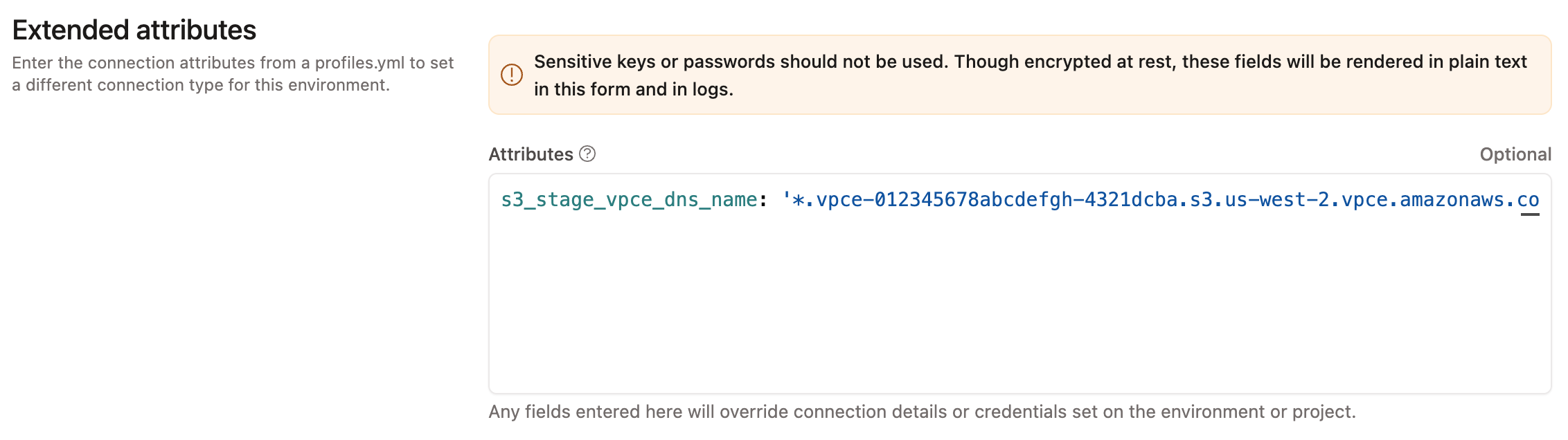
- Obtain the Internal Stage PrivateLink endpoint DNS from dbt Support. For example,
*.vpce-012345678abcdefgh-4321dcba.s3.us-west-2.vpce.amazonaws.com. - In the appropriate dbt project, navigate to Orchestration → Environments.
- In any environment that should use the dbt Internal Stage PrivateLink endpoint, set an Extended Attribute similar to the following:
s3_stage_vpce_dns_name: '*.vpce-012345678abcdefgh-4321dcba.s3.us-west-2.vpce.amazonaws.com'
- Save the changes.
Configuring network policies
If your organization uses Snowflake Network Policies to restrict access to your Snowflake account, you need to add a network rule for dbt.
You can request the VPCE IDs from dbt Support, that you can use to create a network policy. If creating an endpoint for Internal Stage, the VPCE ID will be different from the VPCE ID of the main service endpoint.
For guidance on protecting both the Snowflake service and Internal Stage consult the Snowflake network policies and network rules docs.
Using the UI
Open the Snowflake UI and take the following steps:
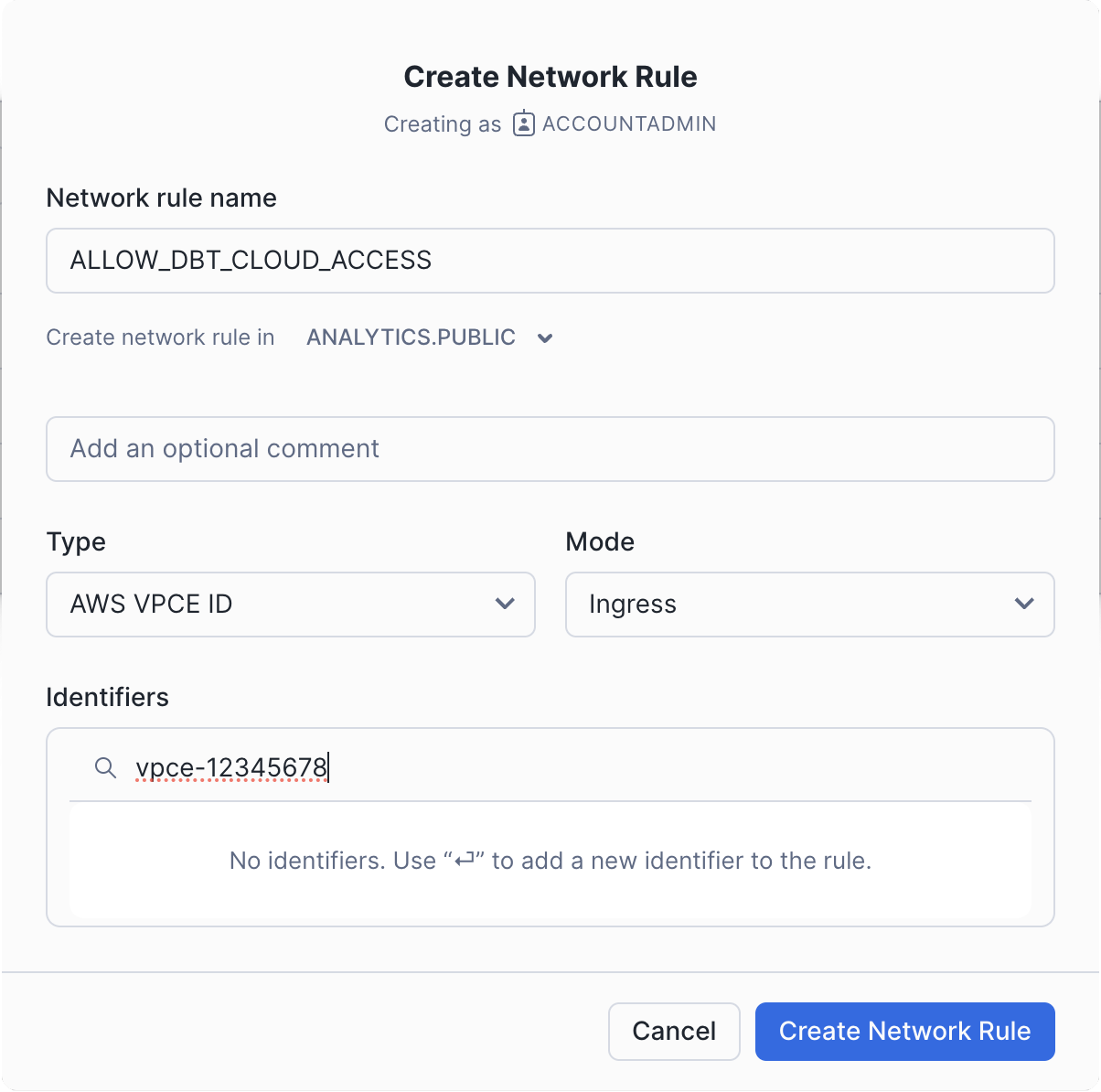
- Go to the Security tab.
- Click on Network Rules.
- Click on Add Rule.
- Give the rule a name.
- Select a database and schema where the rule will be stored. These selections are for permission settings and organizational purposes; they do not affect the rule itself.
- Set the type to
AWS VPCE IDand the mode toIngress. - Type the VPCE ID provided by dbt Support into the identifier box and press Enter.
- Click Create Network Rule.
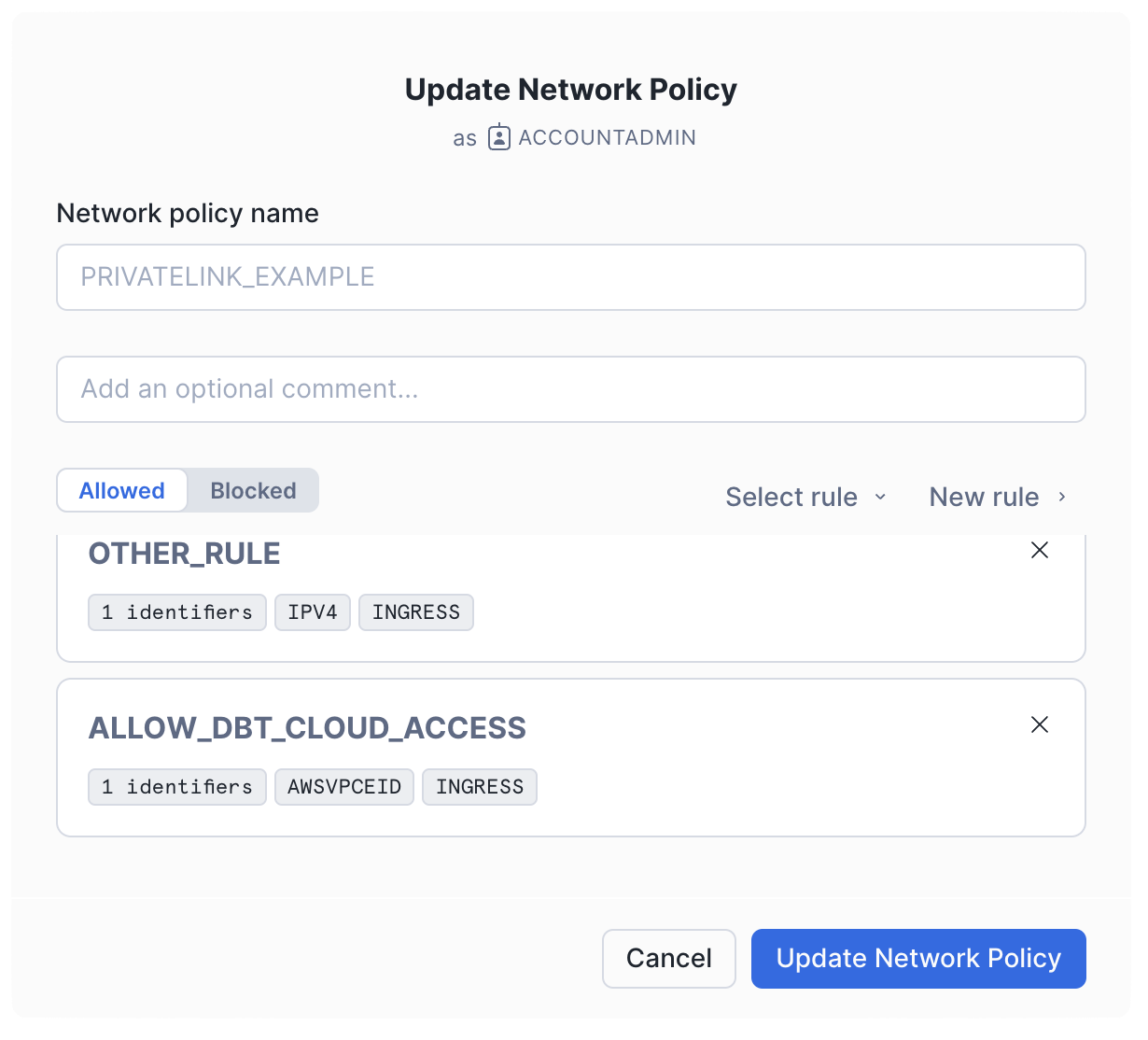
-
In the Network Policy tab, edit the policy you want to add the rule to. This could be your account-level policy or a policy specific to the users connecting from dbt.
-
Add the new rule to the allowed list and click Update Network Policy.
Using SQL
For quick and automated setup of network rules via SQL in Snowflake, the following commands allow you to create and configure access rules for dbt. These SQL examples demonstrate how to add a network rule and update your network policy accordingly.
- Create a new network rule with the following SQL:
CREATE NETWORK RULE allow_dbt_cloud_access
MODE = INGRESS
TYPE = AWSVPCEID
VALUE_LIST = ('<VPCE_ID>'); -- Replace '<VPCE_ID>' with the actual ID provided
- Add the rule to a network policy with the following SQL:
ALTER NETWORK POLICY <network_policy_name>
ADD ALLOWED_NETWORK_RULE_LIST =('allow_dbt_cloud_access');
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.