Set up external OAuth with Redshift EnterpriseEnterprise +
This feature is currently only available for Okta and Entra ID identity providers.
dbt Enterprise and Enterprise+ plans support OAuth authentication with external providers. When External OAuth is enabled, users can authorize their Development credentials using single sign-on (SSO) via the identity provider (IdP). External OAuth authorizes users to access multiple applications, including dbt, without sharing their static credentials with the service. This makes the process of authenticating for development environments easier for the user and provides an additional layer of security to your dbt account.
Getting started
The process of setting up external OAuth will require a little bit of back-and-forth between your dbt, IdP, and data warehouse accounts, and having them open in multiple browser tabs will help speed up the configuration process:
- dbt: You’ll primarily be working in the Account settings —> Integrations page. You will need proper permission to set up the integration and create the connections.
- Identity providers:
- Okta: You’ll be working in multiple areas of the Okta account, but you can start in the Applications section. You will need permissions to create an application and an authorization server.
- Entra ID An admin with access to create Entra ID apps who is also a user in the data warehouse is required.
- Data warehouse:
- Redshift: Create and manage the Identity Center integration with your identity provider.
If the admins that handle these products are all different people, it’s better to have them coordinating simultaneously to reduce friction.
Ensure your Amazon admins have completed the Amazon Identity Center integration with Okta or Entra ID.
Identity provider configuration
Select a supported identity provider (IdP) for instructions on configuring external OAuth in their environment and completing the integration in dbt:
- Okta
- Entra ID
1. Initialize the dbt settings
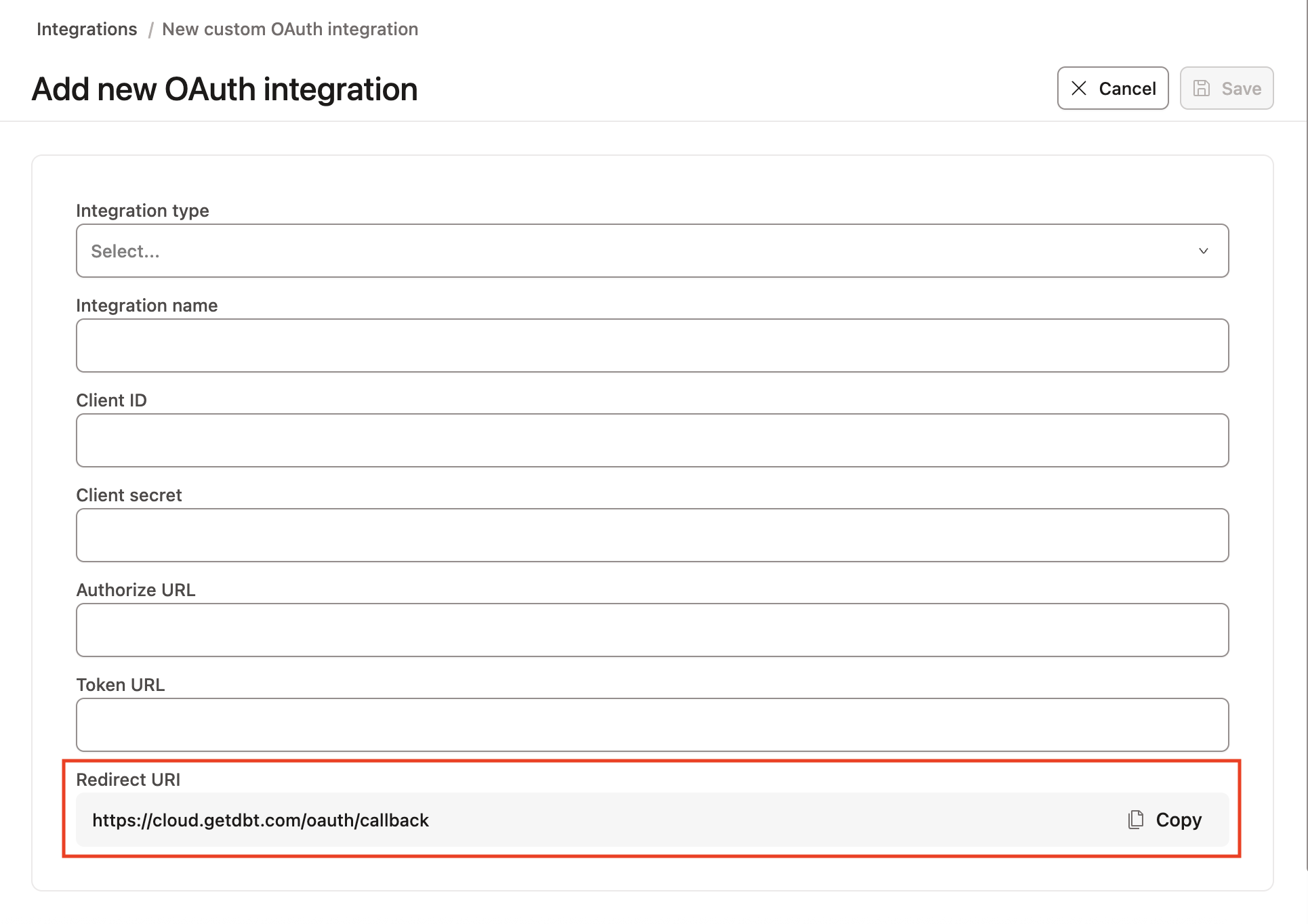
- In your dbt account, navigate to Account settings —> Integrations.
- Scroll down to Custom integrations and click Add integrations
- Leave this window open. You can set the Integration type to Okta and note the Redirect URI at the bottom of the page. Copy this to your clipboard for use in the next steps.
2. Create the Okta app
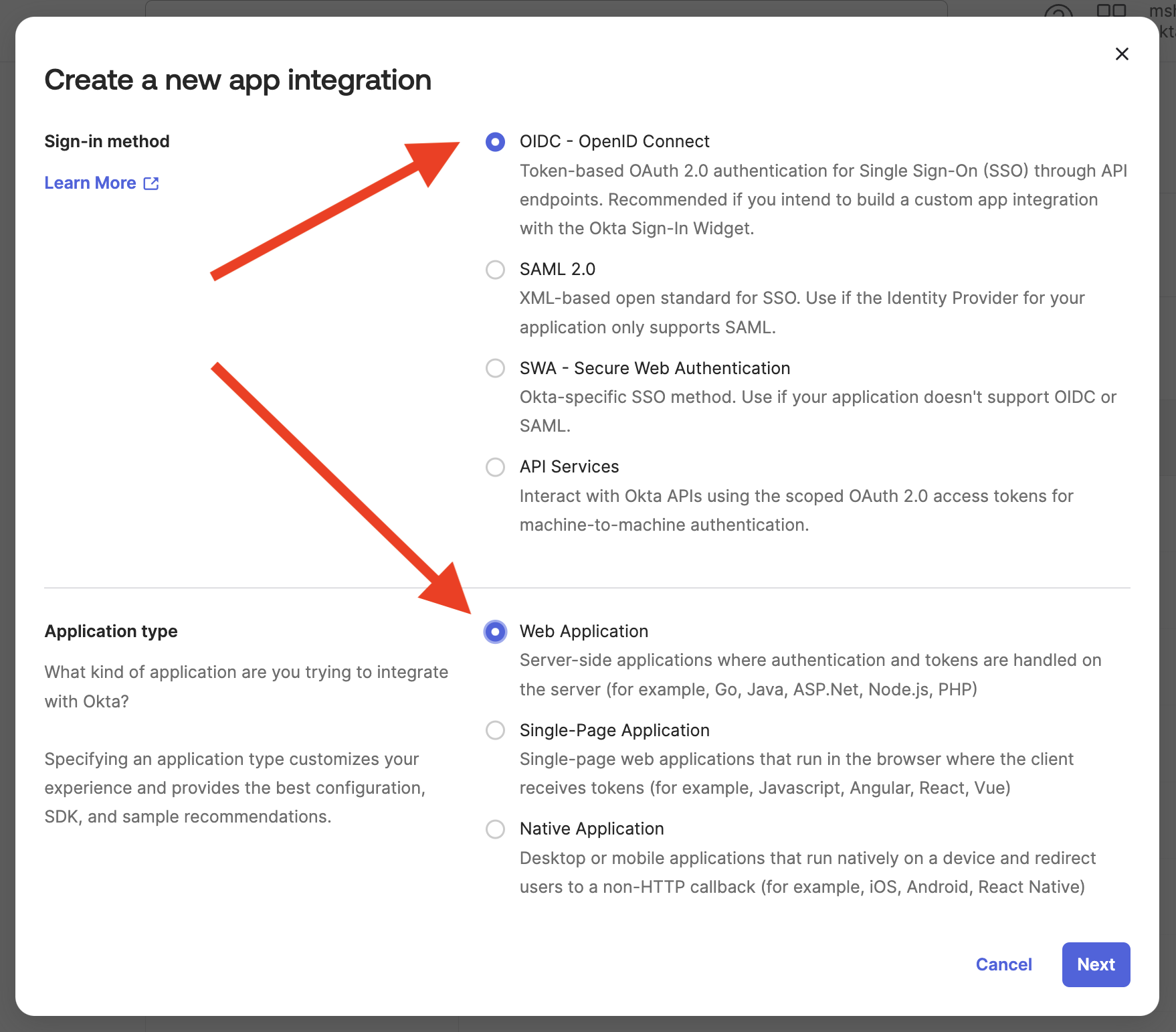
- Expand the Applications section from the Okta dashboard and click Applications. Click the Create app integration button.
- Select OIDC as the sign-in method and Web applications as the application type. Click Next.
- Give the application an appropriate name, something like “External OAuth app for dbt,” that will make it easily identifiable.
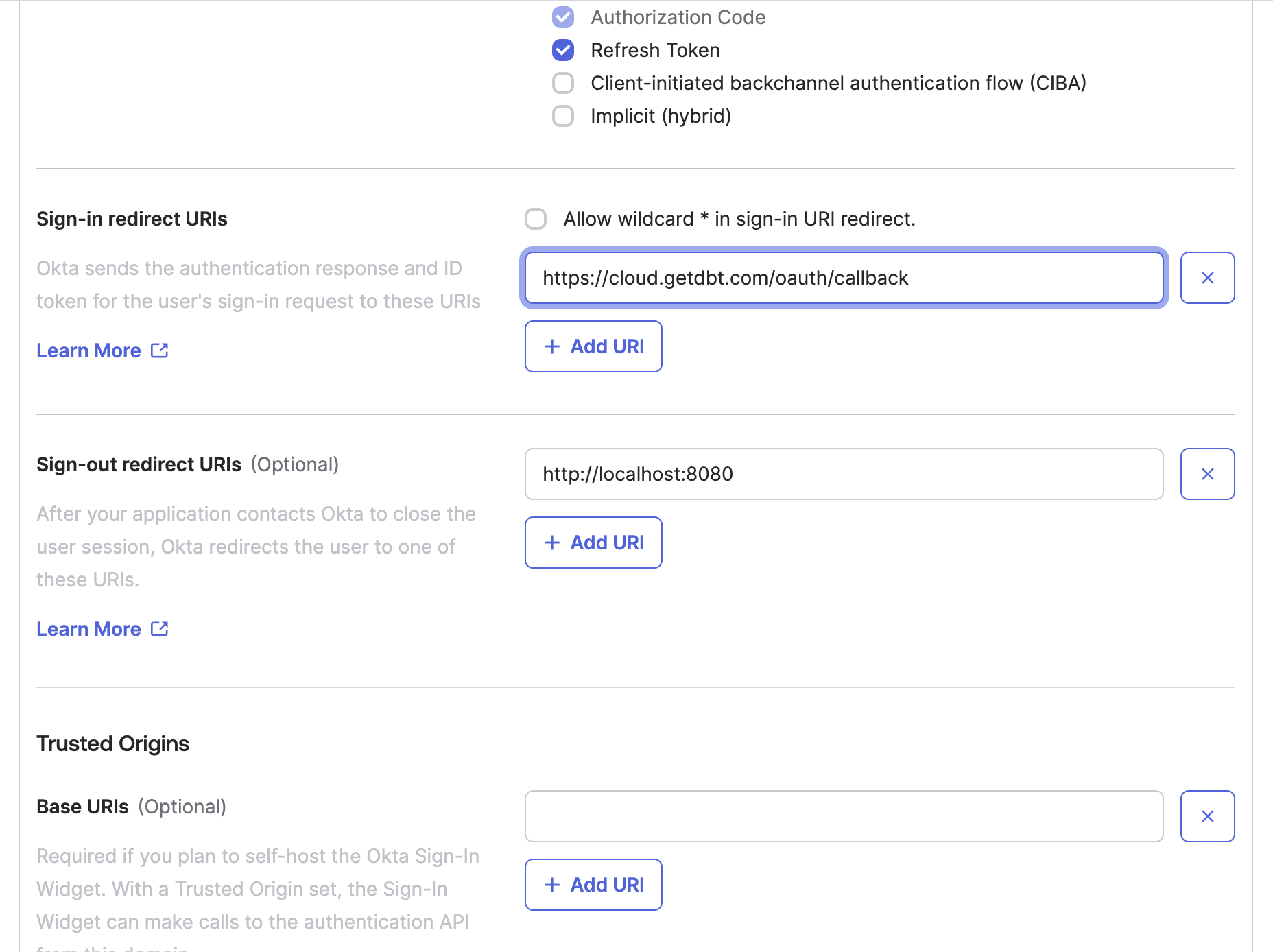
- In the Grant type section, enable the Refresh token option.
- Scroll down to the Sign-in redirect URIs option. You’ll need to paste the redirect URI you gathered from dbt in step 1.3.
- Save the app configuration. You’ll come back to it, but move on to the next steps for now.
3. Create the Okta API
- Expand the Security section and click API from the Okta sidebar menu.
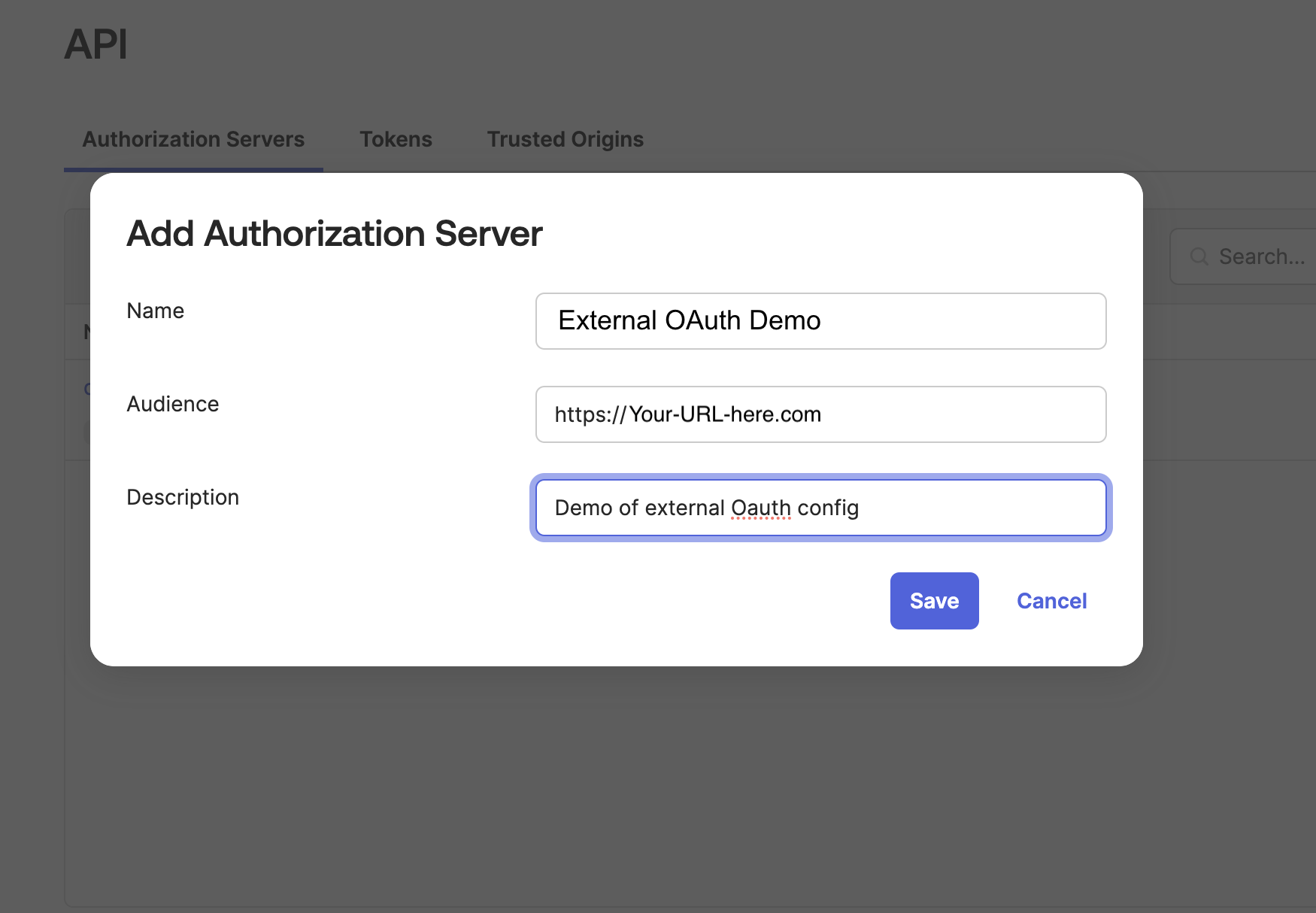
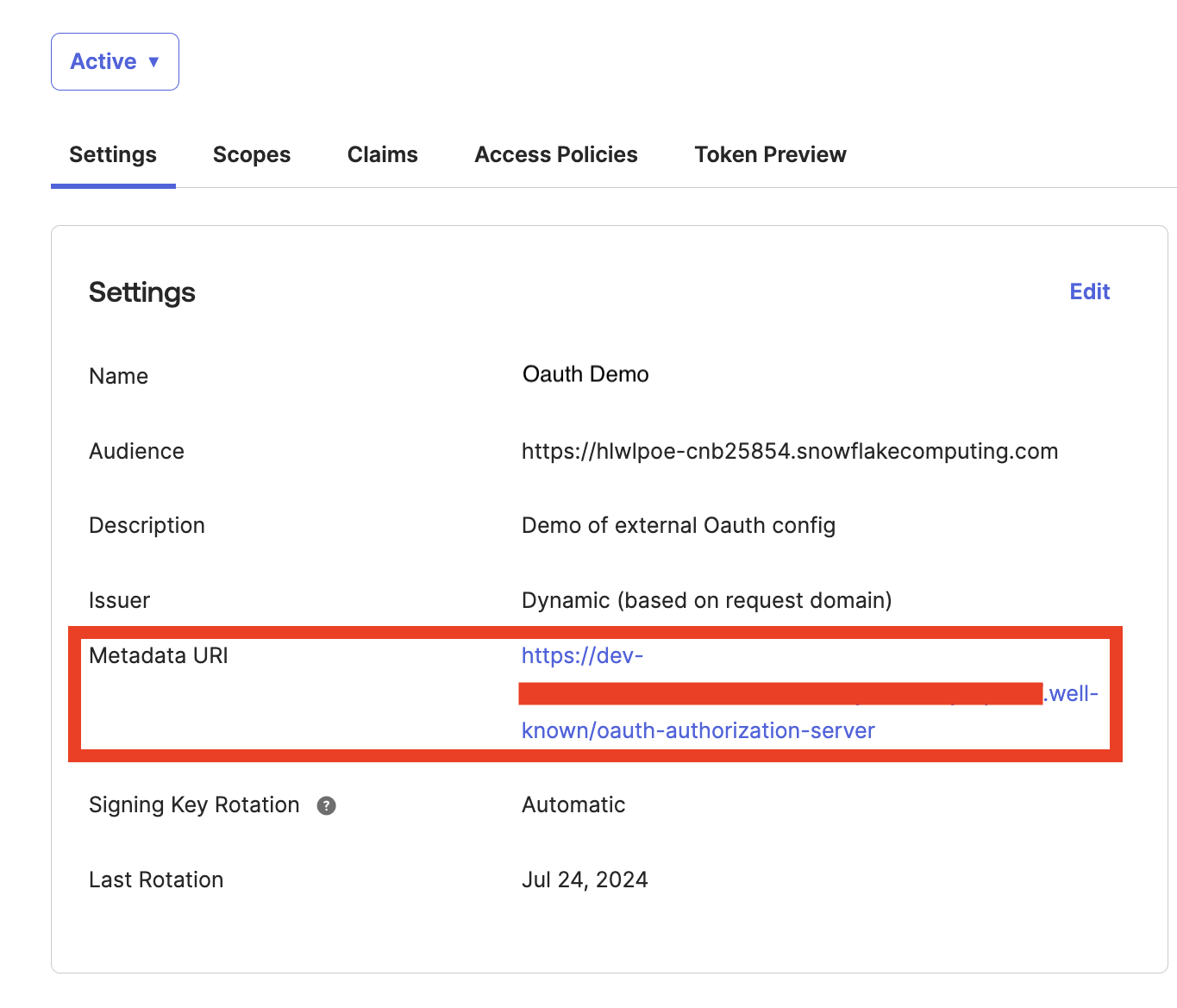
- On the API screen, click Add authorization server. Give the authorization server a name (a nickname for your data warehouse account would be appropriate). For the Audience field, copy and paste your data warehouse login URL. Give the server an appropriate description and click Save.
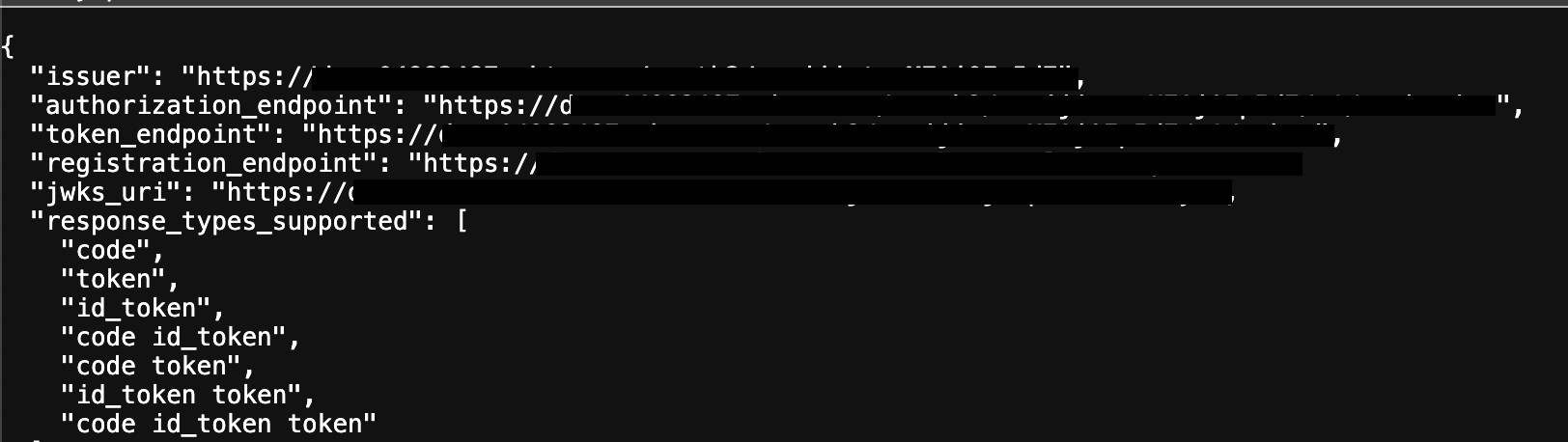
- On the authorization server config screen, open the Metadata URI in a new tab. You’ll need information from this screen in later steps.
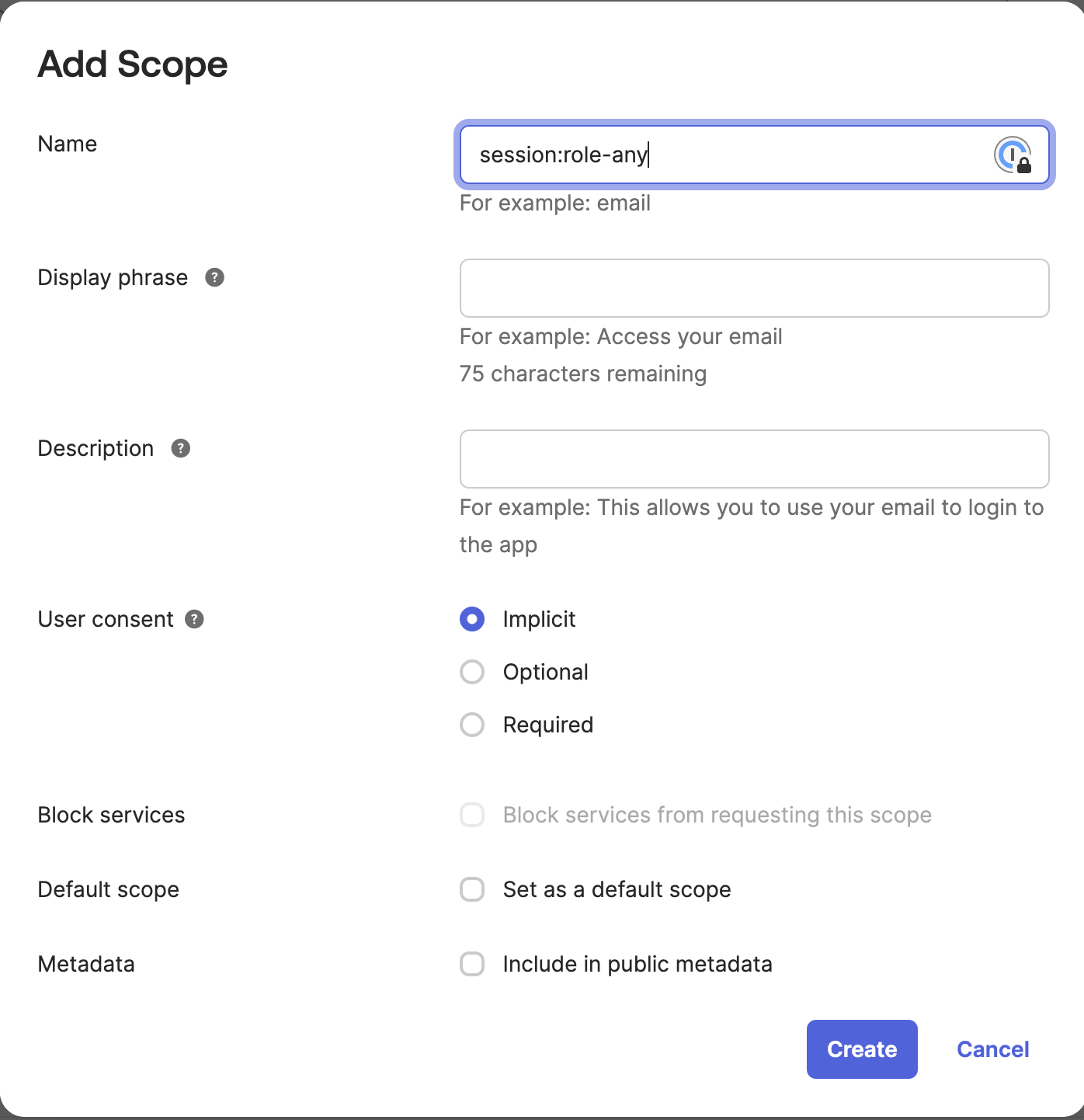
- Click on the Scopes tab and Add scope. In the Name field, add
session:role-any. (Optional) Configure Display phrase and Description and click Create.
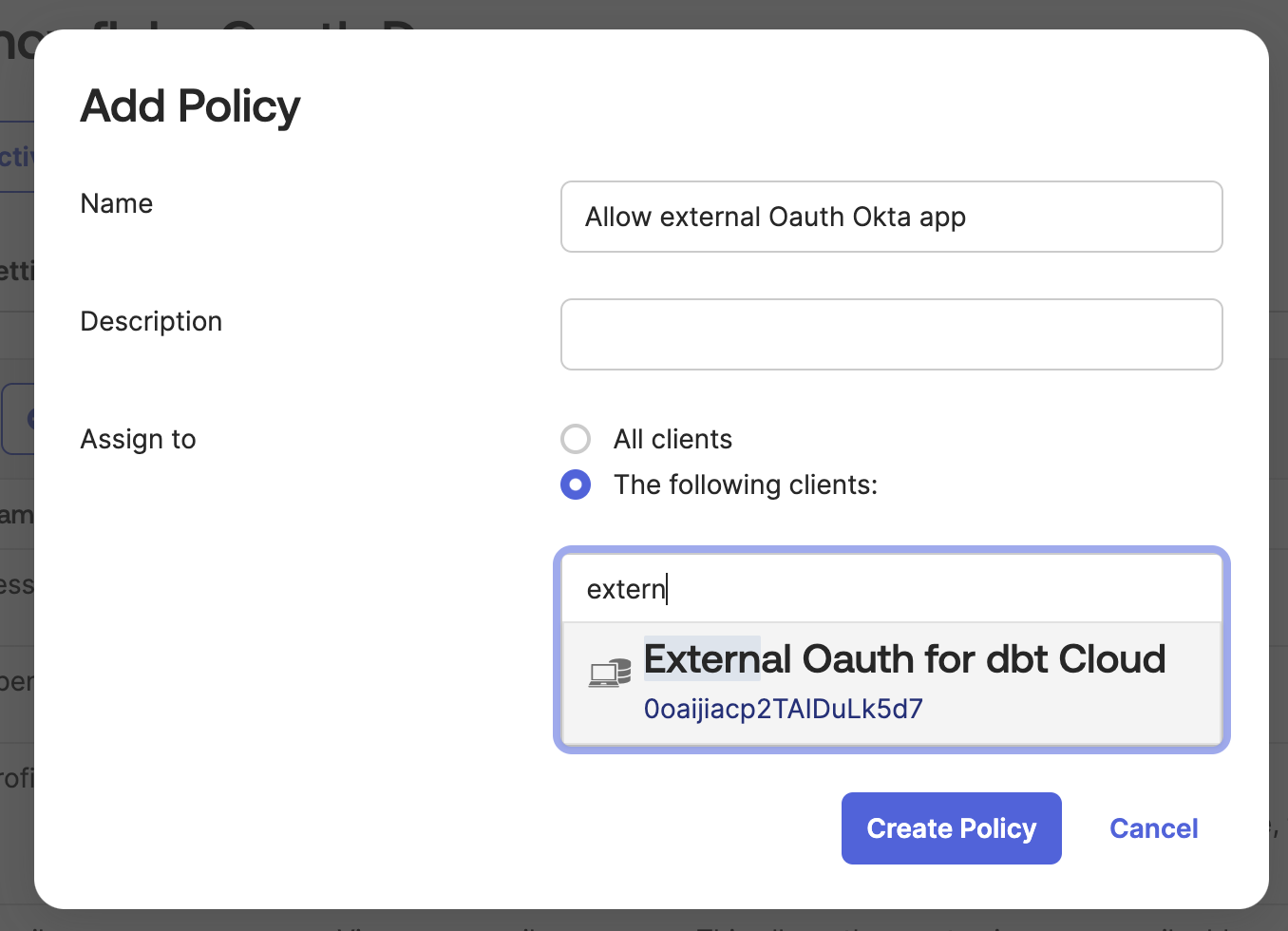
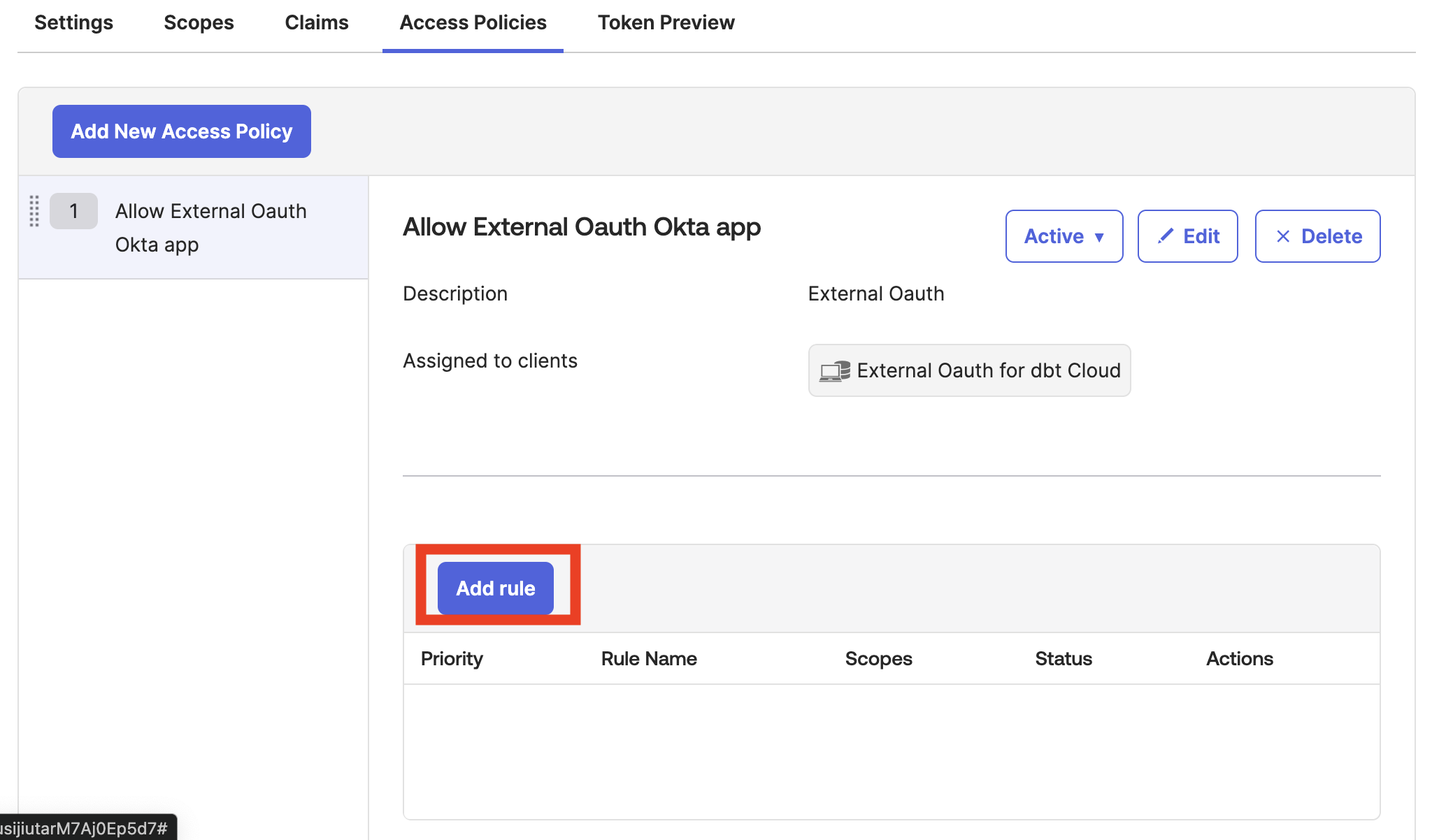
- Open the Access policies tab and click Add policy. Give the policy a Name and Description and set Assign to as The following clients. Start typing the name of the app you created in step 2.3, and you’ll see it autofill. Select the app and click Create Policy.
- On the access policy screen, click Add rule.
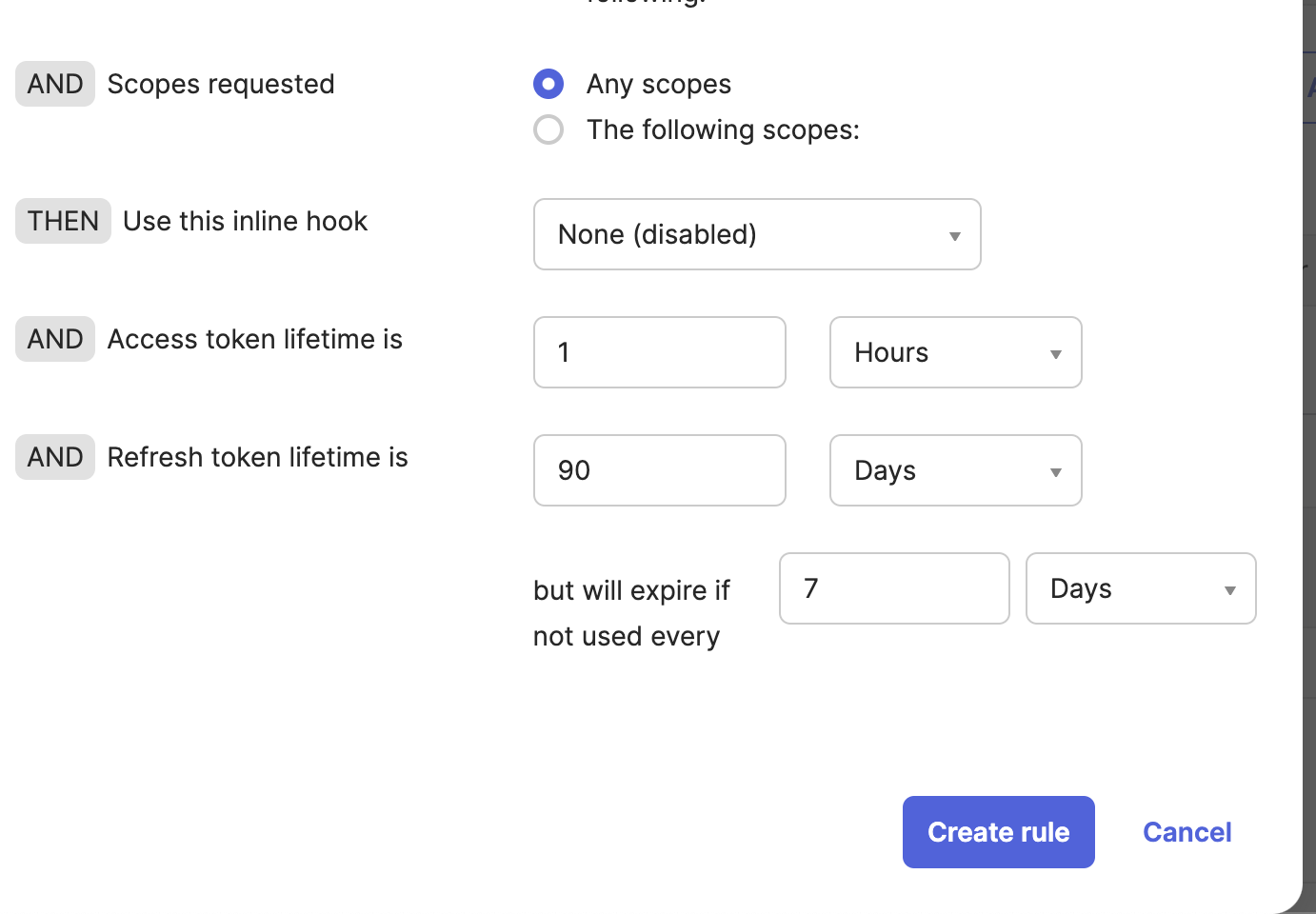
- Give the rule a descriptive name and scroll down to token lifetimes. Configure the Access token lifetime is, Refresh token lifetime is, and but will expire if not used every settings according to your organizational policies. We recommend the defaults of 1 hour and 90 days. Stricter rules increase the odds of your users having to re-authenticate.
- Navigate back to the Settings tab and leave it open in your browser. You’ll need some of the information in later steps.
4. Create the OAuth settings in the data warehouse
Ensure your Amazon admins have completed the Identity Center integration with Okta.
Configure the Okta application and APIs in accordance with your Amazon configs.
5. Configuring the integration in dbt
-
Navigate back to the dbt Account settings —> Integrations page you were on at the beginning. It’s time to start filling out all of the fields.
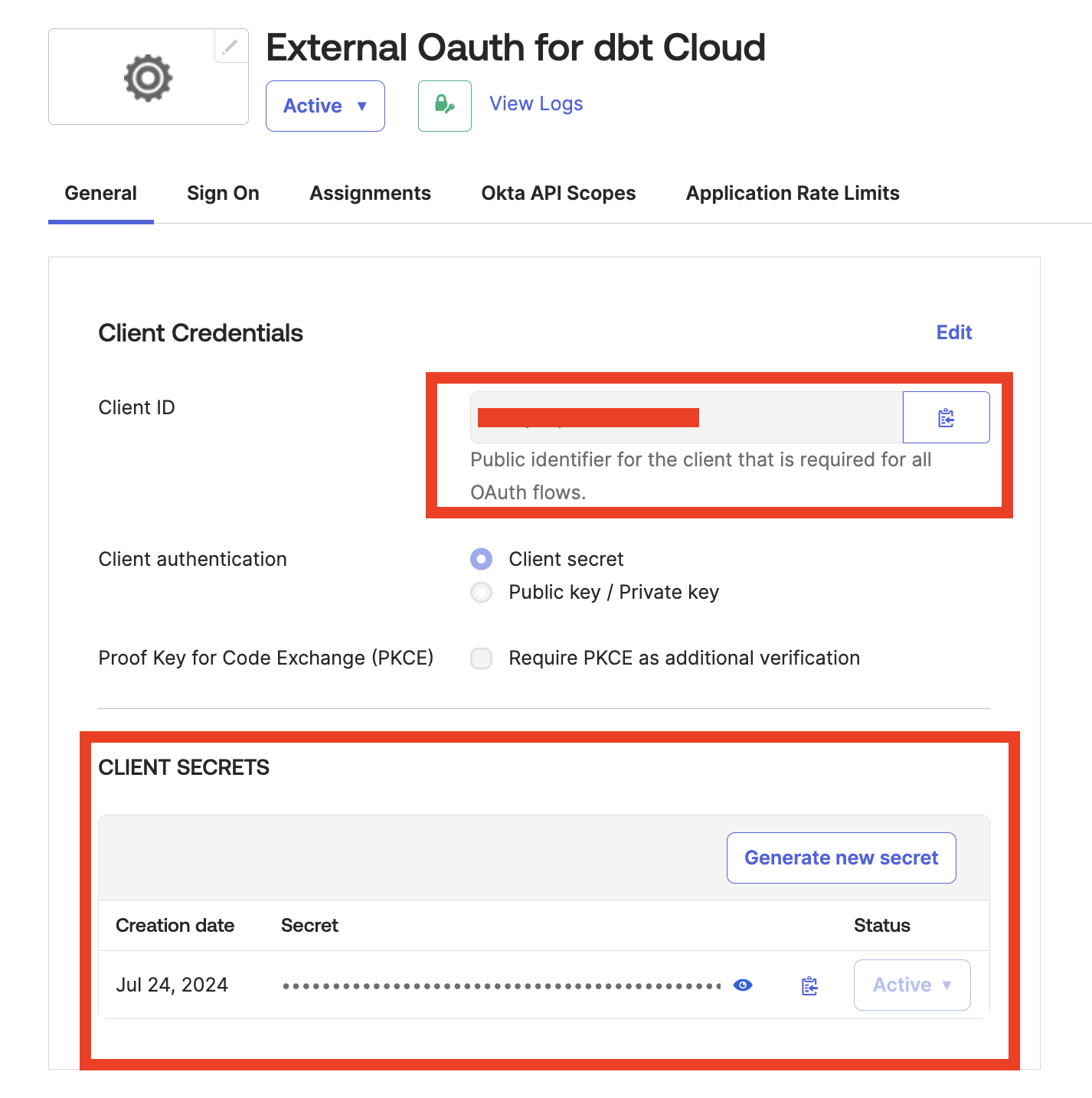
Integration name: Give the integration a descriptive name that includes identifying information about the Okta environment so future users won’t have to guess where it belongs.Client IDandClient secrets: Retrieve these from the Okta application page.
- Authorize URL and Token URL: Found in the metadata URI.
-
Save the configuration
6. Create a new connection in dbt
- Navigate to Account settings and click Connections from the menu. Click New connection.
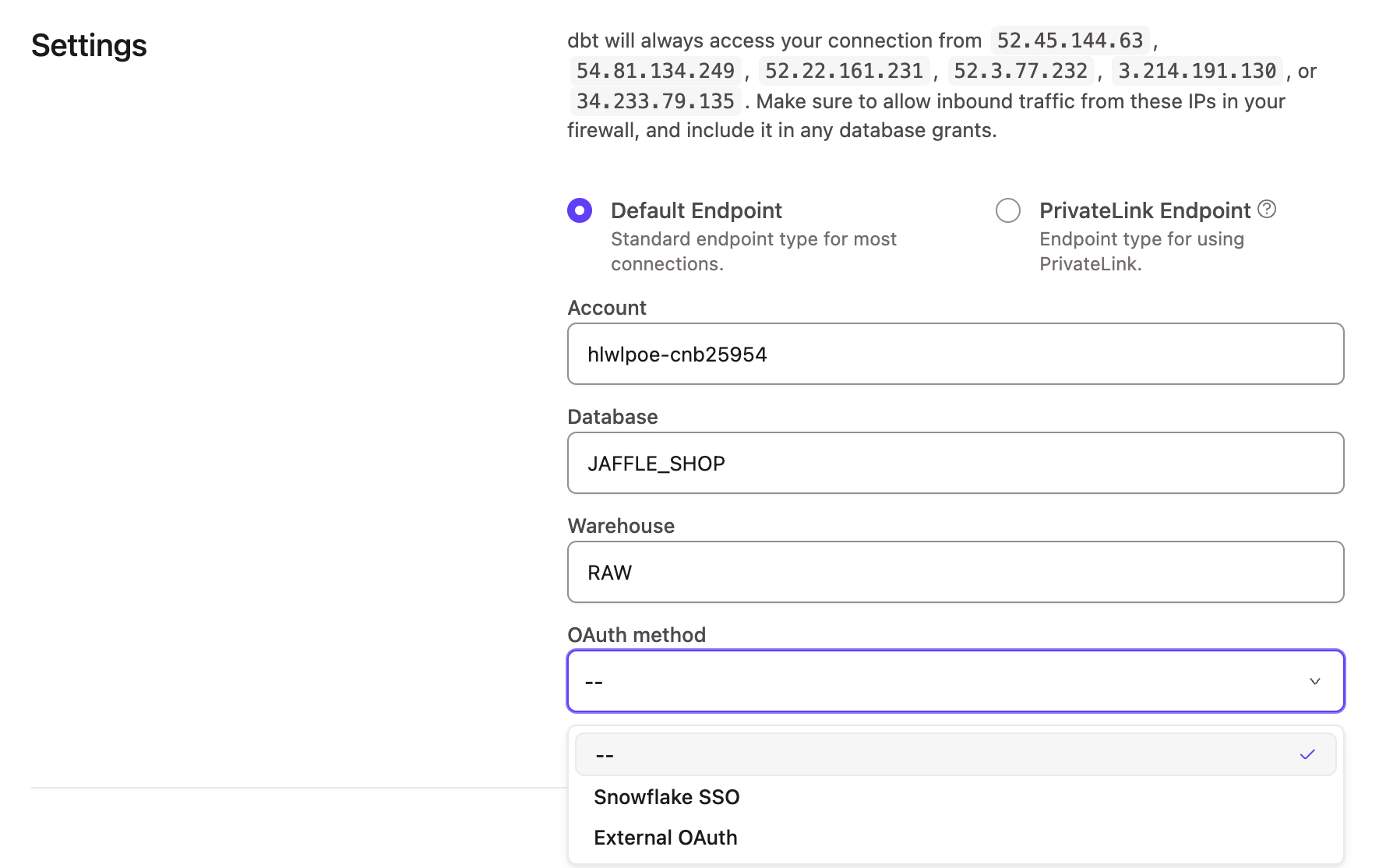
- Configure the
Account,Database, andWarehouseas you normally would, and for theOAuth method, select the external OAuth you just created.
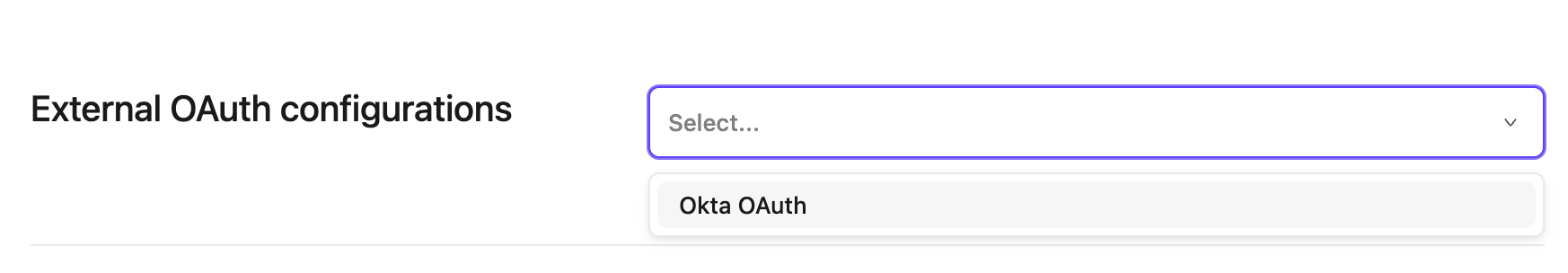
- Scroll down to the External OAuth configurations box and select the config from the list.
- Save the connection, and you have now configured External OAuth with Okta!
1. Initialize the dbt settings
- In your dbt account, navigate to Account settings —> Integrations.
- Scroll down to Custom integrations and click Add integrations.
- Leave this window open. You can set the Integration type to Entra ID and note the Redirect URI at the bottom of the page. Copy this to your clipboard for use in the next steps.
2. Create the Entra ID apps
You’ll create two apps in the Azure portal: A resource server and a client app.
Create a resource server
In your Entra ID account:
-
From the app registrations screen, click New registration.
- Give the app a name.
- Ensure Supported account types are set to “Accounts in this organizational directory only (
Org name- Single Tenant).” - Click Register to see the application’s overview.
-
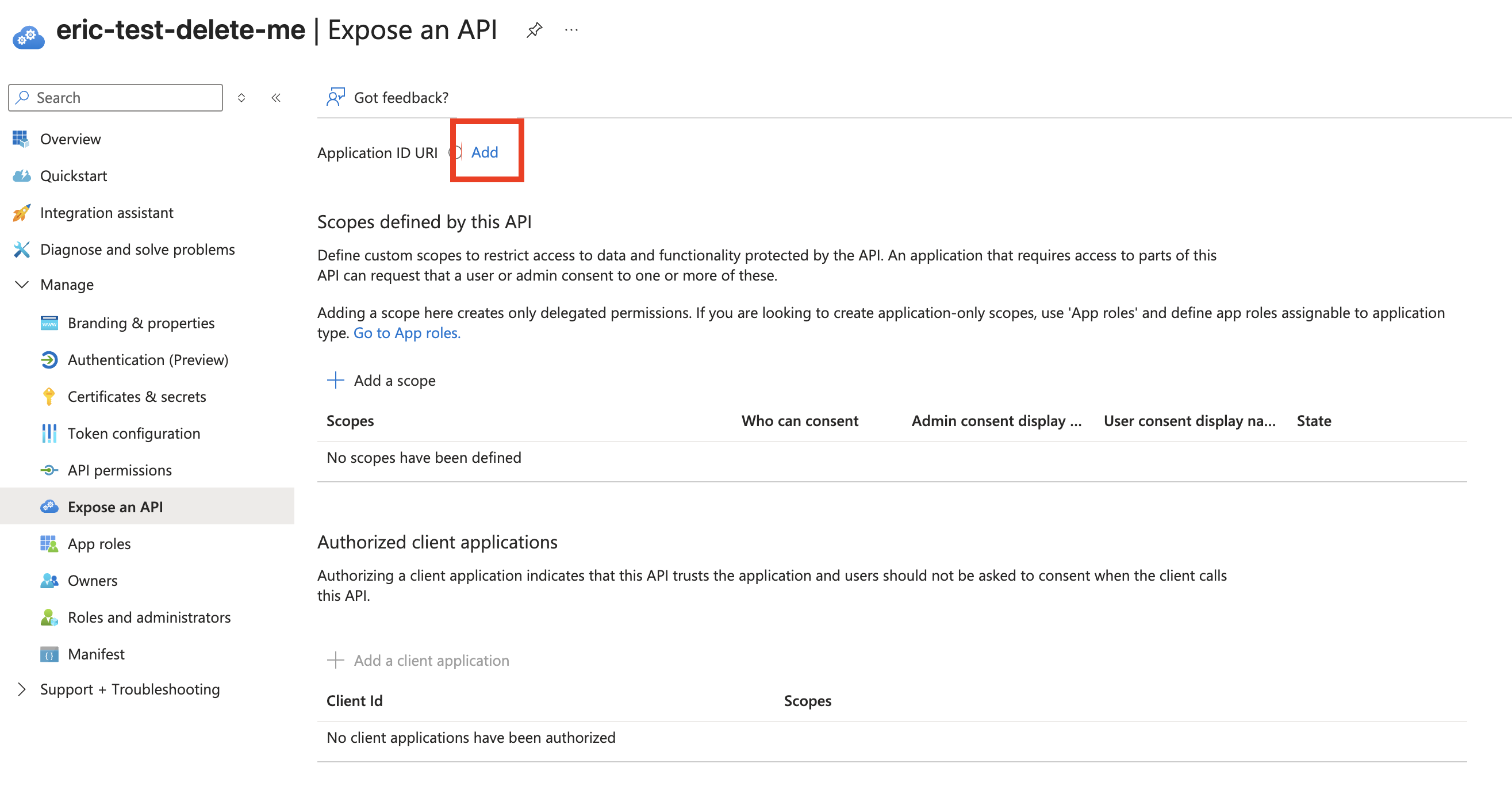
From the app overview page left menu, click Expose an API.
-
Click Add next to Application ID URI. The field will automatically populate.
-
Click Save.
-
Record the
valuefield for use in a future step. -
From the same screen, click Add scope:
- Name the scope
dbt-redshift. - Set Who can consent? to Admins and users.
- Set Admin consent display name to
dbt-redshiftand give it a description. - Ensure State is set to Enabled.
- Click Add scope.
- Name the scope
Create a client app
-
From the App registration page, click New registration.
- Give the app a name that uniquely identifies it as the client app.
- Ensure Supported account types are set to “Accounts in this organizational directory only (
Org name- Single Tenant).” - Set the Redirect URI to Web and copy/paste the Redirect URI from dbt into the field.
- Click Register.
-
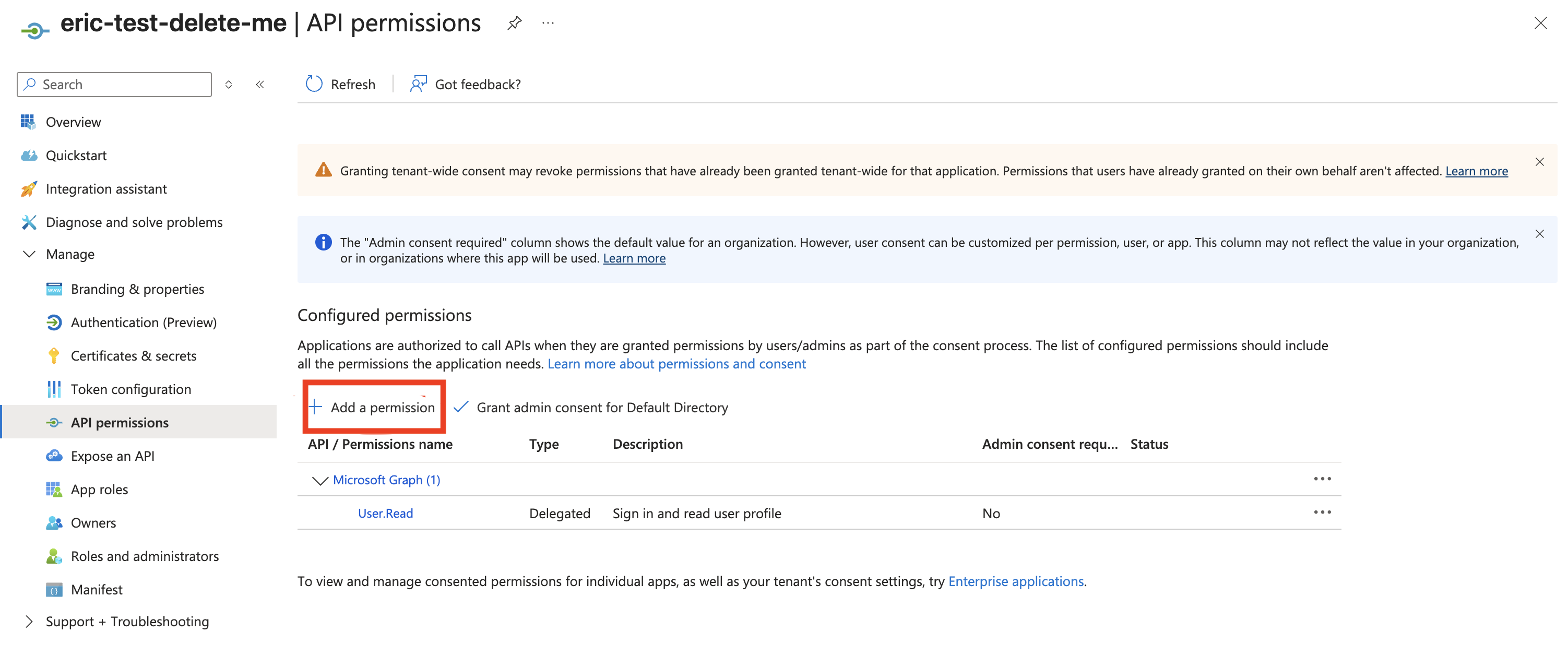
From the app overview page, click API permissions from the left menu, and click Add permission.
-
From the pop-out screen, click APIs my organization uses, search for the resource server name from the previous steps, and click it.
-
Ensure the box for the Permissions
dbt-redshiftis enabled and click Add permissions. -
Click Grant admin consent and from the popup modal click Yes.
-
From the left menu, click Certificates and secrets and click New client secret. Name the secret, set an expiration, and click Add.
- Note: Microsoft does not allow “forever” as an expiration date. The maximum time is two years. Documenting the expiration date so you can refresh the secret before the expiration or user authorization fails is essential.
-
Record the
valuefor use in a future step and record it immediately.- Note: Entra ID will not display this value again once you navigate away from this screen.
3. Configuring the integration in dbt
- Navigate back to the dbt Account settings —> Integrations page you were on at the beginning. It’s time to start filling out all of the fields. There will be some back-and-forth between the Entra ID account and dbt.
Integration name: Give the integration a descriptive name that includes identifying information about the Entra ID environment so future users won’t have to guess where it belongs.Client secrets: Found in the Client ID from the Certificates and secrets page.Valueis theClient secret. Note that it only appears when created; Microsoft hides the secret if you return later, and you must recreate it.Client ID: Copy the’ Application (client) ID’ on the overview page for the client ID app.Authorization URLandToken URL: From the client ID app, open theEndpointstab. These URLs map to theOAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint (v2)andOAuth 2.0 token endpoint (v2)fields. You must use v2 of theOAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint. Do not use V1. You can use either version of theOAuth 2.0 token endpoint.Application ID URI: Copy theApplication ID URIfield from the resource server’s Overview screen.
Configure the Trusted Token Issuer in IAM IdC
A trusted token issuer generates an access token that is used to identify a user, and then authenticates that user. This essentially lets services outside of the AWS ecosystem, such as the dbt platform, connect to IAM IdC (and Redshift) with access tokens they have generated or retrieved from an external IdP (Entra ID or Okta).
The following steps are outlined per this blog post:
- Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to IAM Identity Center, and then to the Settings.
- Select the Authentication tab and under Trusted token issuers, choose Create trusted token issuer.
- On the Set up an external IdP to issue trusted tokens page, under Trusted token issuer details, do the following:
- For Issuer URL, enter the OIDC discovery URL of the external IdP that will issue tokens for trusted identity propagation. Include the forward slash at the end of the URL.
- For Trusted token issuer name, enter a name to identify this TTI in IAM Identity Center and the application console.
- Under Map attributes, do the following:
- For Identity provider attribute, select an attribute from the list to map to an attribute in the Identity Center identity store. You can choose:
- Object Identifier
- Subject
- Other — When using this options with UPN, it's been our experience that
upnmatched up withEmail.
Configure Redshift IdC application to utilize TTI
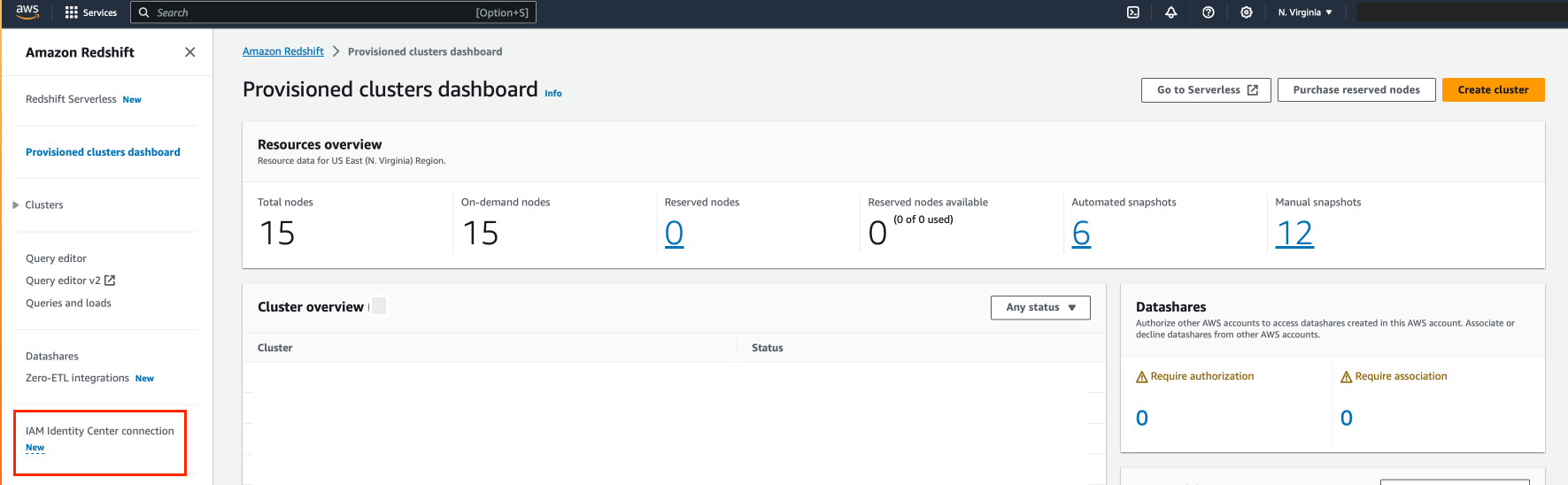
To start, select IAM Identity Center connection from the Amazon Redshift console menu.
- Select the Amazon Redshift application that you created as part of the setup.
- Select the Client connections tab and choose Edit.
- Choose Yes under Configure client connections that use third-party IdPs.
- Select the checkbox for Trusted token issuer that you created in the previous section.
- Enter the aud claim value under Configure selected trusted token issuers. This should be the application ID URI you set for the integration in the dbt platform.
Finalizing the dbt configuration
If you have an existing connection, make sure that the OAuth method is set to External OAuth and select the integration you created in an earlier step. Otherwise, create a new Redshift connection, being sure to set values for:
- Server Hostname
- OAuth Method
- Database name (this field can be found under the Optional Settings)
This connection should be set as the connection for a development environment in an existing or new project.
Once the connection has been assigned to a development environment, you can configure your user credentials for that development environment under Account Settings > Your Profile > Credentials > <Your Project Name>. Set the authentication method to External OAuth, set the schema and other fields if desired, and save the credentials. You can then click the Connect to Redshift button.
Verify connection in Studio
Once your development session has initialized, you can test that you’re able to connect to Redshift using external OAuth by running dbt debug.
Was this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.